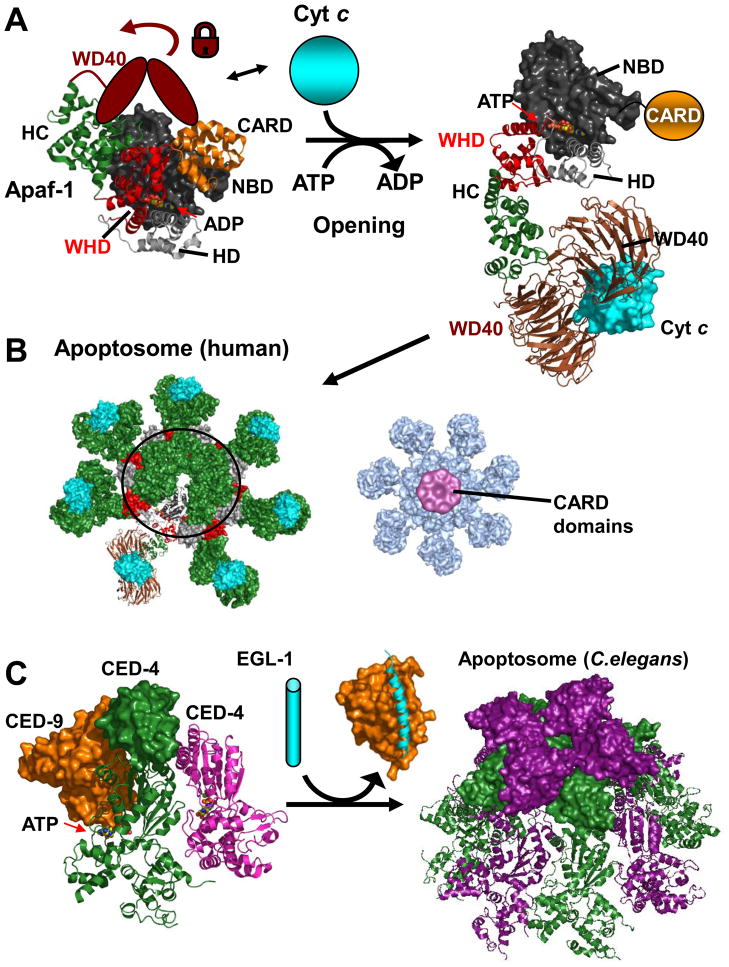
Figure 3. Apoptosomes.
A. Apaf-1 - opening. The structure of monomeric Apaf-1 shows a compact domain arrangement containing a central ADP molecule. Abbreviations are as in the main text and the WD40 region absent from the crystal structure is depicted as a cartoon locking the closed conformation. Cytochrome C releases the lock and ADP/(d)ATP exchange can occur along with a opening of Apaf-1 (inferred from the apoptosome structure under B). The CARD is not included in the electron microscopy structure since it becomes flexibly attached upon opening–illustrated in orange. B. Human Apoptosome. Open and cytochrome C bound Apaf-1 molecules can now interact to form the oligomeric apoptosome. Note that an outer ring is formed by alternating WHD/HD entities. Right: Map of Apoptosome with bound caspase-9 CARD domains. In this 3D map the CARD/CARD complexes hover in a ring-like manner above the apoptosome posed to dimerize and activate the catalytic domains of caspase-9 in the context of full length caspase-9. (PDB accession and structures: monomeric Apaf-1 1z6t, apoptosome based on 3iyt; cytochrome C bound model and density map for CARD bound apoptosome kindly provided by Drs. S. Yuan and C.W. Akey.) C. C. Elegans Apoptosome. CED-9 (orange) binds and inhibits an ATP bound CED-4 dimer (green, magenta; parts of the second CED-4 molecule are not defined in the structure). EGL-1 (cyan) binds and displaces CED-9 releasing the CED-4 dimers that form the octameric C. Elegans apoptosome. CARD domains are displayed in surface representation (PDB accession codes: 2a5y,1ty4, 3lqq)