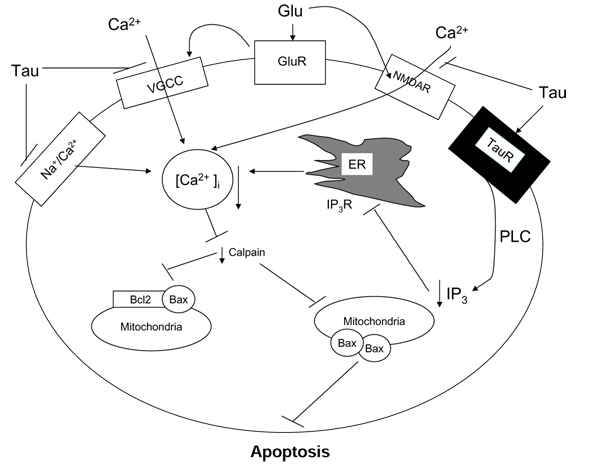
Figure 3.
A model depicting the pathway that taurine exerts its function against glutamate-induced apoptosis. Taurine’s neuroprotective functions are due to its role in reducing intracellular free calcium concentration and its antioxidative stress capacity. Taurine can shift the ratio of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein and pro-apoptotic Bax protein towards cell survival. As shown in the diagram taurine inhibits glutamate-induced activation of calcium and the subsequent heterodimerization of Bcl-2 and Bax protein resulting in the apoptosis cascade.