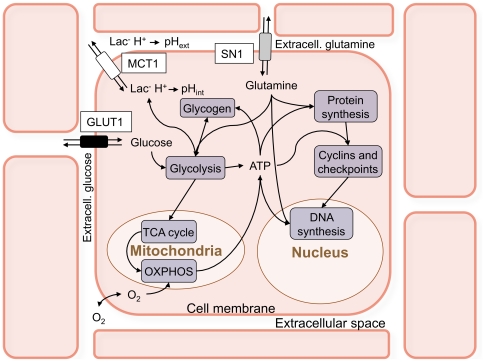
Figure 1. Rough sketch of the biochemical pathways incorporated in the model of single cells.
We take into account the main metabolic pathways (glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation through the TCA cycle and gluconeogenesis), including the role of mitochondria in the production of ATP. The model also includes protein and DNA synthesis, and checkpoints controlled by representative members of the cyclin family. The single-cell model has two spatial compartments (the inside of the cell and its immediate neighborhood, the extracellular space that surrounds it) and transport of substances between these compartments is regulated by transporters on the cell membrane that are also included in the model. The extracellular space of each cell communicates by simple diffusion with the neighboring extracellular spaces and with the environment. The complete map of the biochemical pathways is shown in figure S2.