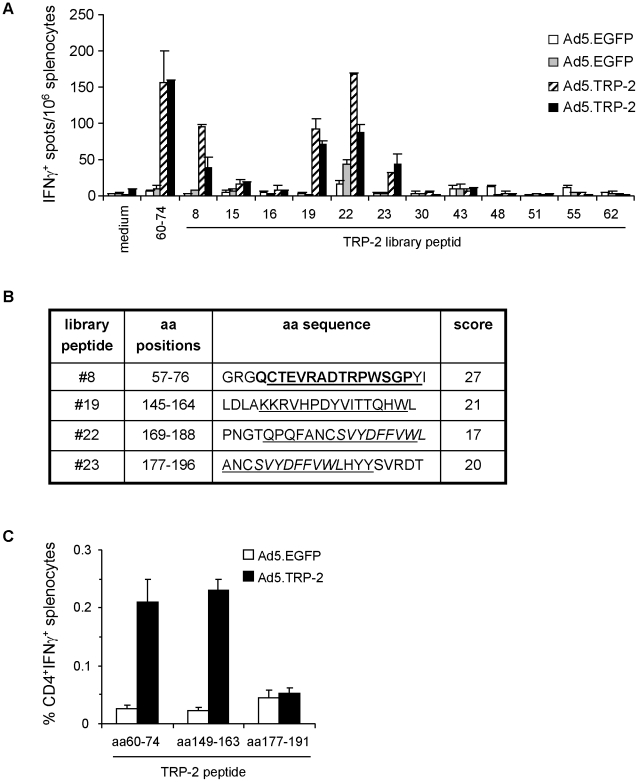
Figure 2. Phenotypic analysis of TRP-2-specific T cell responses induced in Ad5.TRP-2-immunized HLA-DR3tg mice.
A, Spleen cells from HLA-DR3tg mice injected i.p. with 5×108 pfu Ad5.TRP-2 or Ad5.EGFP (2 mice per group) were screened ex vivo by IFN-γ ELISpot assay for reactivity against individual TRP-2-specific library peptides determined by combinatorial analysis. T cell responses of two control mice (Ad5.EGFP) and two TRP-2-immunized mice (Ad5.TRP-2) are represented as individual columns in the diagram. Error bars show standard error of the mean. Experiments were performed three times, yielding similar results. B, Selected TRP-2-derived library peptides #8, #19, #22 and #23 are indicated by amino acid (aa) positions and aa sequence. Peptides were analyzed in silico by the SYFPEITHI algorithm [33] for the presence of predicted HLA-DRB*0301 binding sequences (underlined). Prediction scores for HLA-DRB1*0301-restricted epitopes are listed on the right. Known HLA-DRB1*0301-restricted CD4+ T cell epitopes are typed in bold and the H2-Kb-restricted CTL epitope TRP-2180–188 is written in italics. C, HLA-DR3tg mice received i.p. injections of 5×108 pfu Ad5.TRP-2 or Ad5.EGFP (3 mice per group). Two weeks later spleen cells from infected mice were harvested and stimulated in vitro with the indicated peptides. After 6 days, splenocyte cultures were analyzed for the presence of peptide-reactive T cells by intracellular IFN-γ staining. Stained cells were analyzed by flow cytometry for the percentage of IFN-γ+ CD4+ T cells. Error bars show standard error of the mean of three immunized mice. Experiments were performed three times yielding similar results.