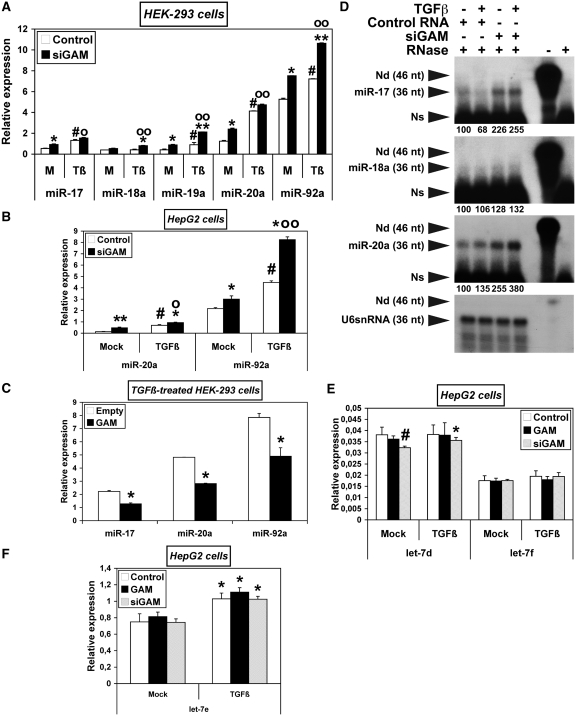
Figure 6.
GAM opposes the upregulation of miR-17-92 miRNAs by TGFβ effectors. (A–C) HEK-293 (A and C) or HepG2 cells (B) were transfected with either a control RNA or siGAM (A and B), or with the empty pCMV-HA vector or pCMV-HA-GAM (C). After 34 h, they were either mock-treated (A and B) or treated with TGFβ (A–C) as indicated. The relative levels of the indicated miRNAs were determined by qRT–PCR. Values represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). The results obtained with mock-treated samples (M) in (A) are the same as those in Figure 3B. They are presented again along with the results obtained with TGFβ-treated samples (Tβ) for easier comparison, as they were drawn from the same experiment. Panel A: * and **, siGAM significantly different from Control RNA for each treatment, *, P < 0.005, **, P < 0.0005; #, TGFβ-treated Control RNA significantly different from mock-treated Control RNA, P < 0.0002; o and oo, TGFβ-treated siGAM significantly different from mock-treated siGAM, o, P < 0.003, oo, P < 0.0004. Panel B: * and **, siGAM significantly different from Control RNA for each treatment, *, P < 0.05, **, P < 0.002; #, TGFβ-treated Control RNA significantly different from mock-treated Control RNA, P < 0.02; o and oo, TGFβ-treated siGAM significantly different from mock-treated siGAM, o, P < 0.02, oo, P < 0.01. Panel C: *, Significantly different from Empty control vector, P < 0.05. (D) The relative levels of miR-17, miR-18a and miR-20a were determined by RNase-protection assays. Total RNAs extracted from HepG2 cells (10 µg per assay) treated and transfected as indicated (four left lanes) were hybridized with a radiolabelled RNA antisense probe complementary to the indicated miRNAs. The lengths of the antisense miR-17, miR-18a and miR-20a probes were made equal to that of the U6snRNA antisense probe by addition of a 3′-poly(A)-tail. Namely, the RNases used in the assay (RNase 1 and RNase T1) are not able to cut phosphodiester bonds following a non-paired A nt. The relative intensities of the protected fragments, given under each panel in percent of the control sample (lane 1), were calculated using the U6snRNA as an internal control. The efficiency of RNase digestion was assessed in parallel following the incubation of each probe with 10 µg yeast tRNAs (two rights lanes). ‘-RNase’ controls correspond to a 15-fold dilution of the undigested samples. Exposure time at −80°C was 36 h for miR-17, miR-18a and miR-20a probes, and 2 h for U6snRNA probe. Nd, non-digested, Ns, non-specific. (E,F) HepG2 cells were transfected with either a pCMV-HA/Control RNA mix (Control), a pCMV-HA-GAM/Control RNA mix (GAM) or a pCMV-HA/siGAM mix (siGAM). 34 h later, they were either mock-treated or treated with TGFβ. The relative levels of let-7d and let-7f (E) and of let-7e (F) were determined by qRT–PCR. Values represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). Panel E: #, mock-treated siGAM significantly different from mock-treated Control, P = 0.01; *, TGFβ-treated siGAM significantly different from mock-treated siGAM, P = 0.03. Panel F: *, Significantly different from the corresponding mock-treated sample, *, P < 0.02.