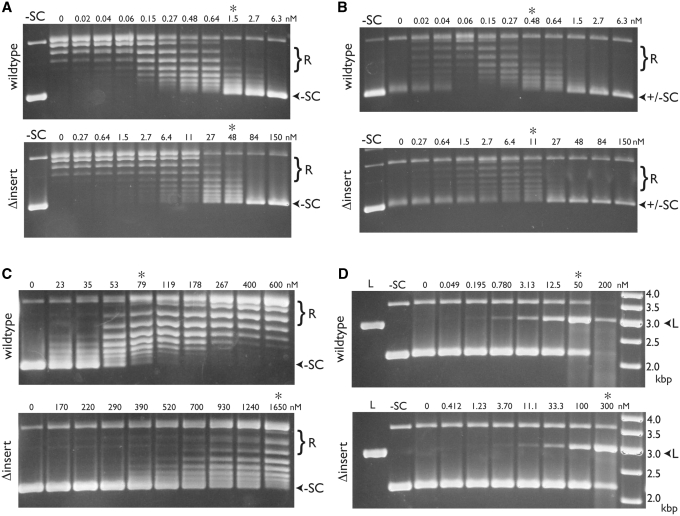
Figure 5.
Comparison of wild-type and GyrBΔinsert gyrase activities. Negative supercoiling assays (A), positive supercoil relaxation assays (B), negative supercoil relaxation assays (C) and ciprofloxacin-dependent DNA cleavage assays (D) were carried out as described (‘Materials and Methods’ section). The enzyme (wild-type or GyrBΔinsert gyrase) used in each titration is shown at left. Positions of relaxed and supercoiled species are indicated at right. Lanes with negatively supercoiled (–SC) or BamHI-linearized (L) plasmid standards are indicated, as are the concentrations of gyrase tetramer (in nM). Asterisks indicate lanes in each pair of gels with comparable activities. In the cleavage assay (D), the rightmost lane contains a DNA ladder (O’GeneRuler, Fermentas) with the standard sizes (in kb) indicated.