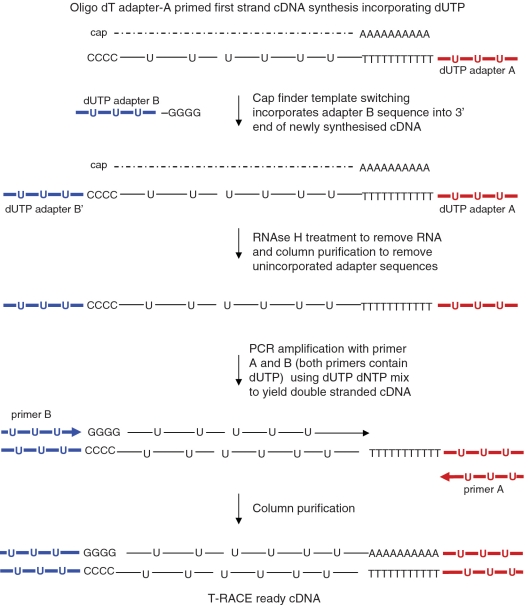
Figure 1.
Diagrammatic representation of double-stranded template (T-RACE cDNA) synthesis protocol. First-strand cDNA synthesis using a dNTP mix that includes dUTP is primed using an oligo-dT adapter-A primer. After reaching the 5′ end of the mRNA (dashed line), oligo(dC) is added to the end of the cDNA by the MMLV reverse transcriptase. Base pairing between the oligo(dC) and the oligo(dG) of adapter-B occurs, and through the process of template switching, the reverse compliment of adapter-B (adapter B′) is incorporated into the 3′ end of the newly synthesized cDNA as previously described (4,5). Adapters A and B both contain dUTP instead of dTTP. Adapters A and B serve as priming sites for PCR amplification using primers A and B, which also have dTTP replaced by dUTP. PCR is performed using a dNTP mix that contains dUTP, so the resulting double-stranded cDNA (T-RACE ready cDNA) contains dUTP residues throughout and dUTP-containing adapters at the 3′ and 5′ ends.