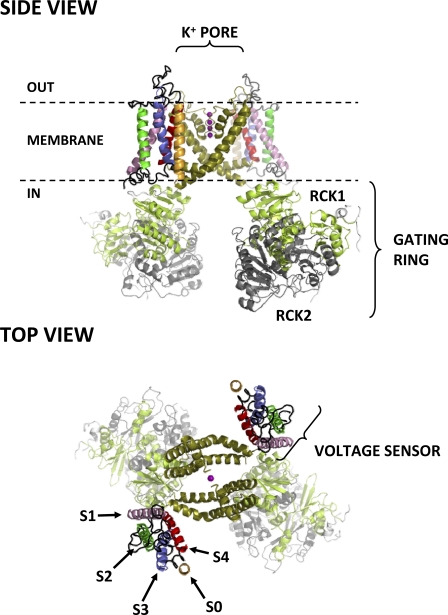
Figure 1.
Side and top views of the putative structure of the BKCa channel. Only two out of four α subunits are shown for clarity. Each α subunit consists of seven transmembrane segments (S0–S6) and a large intracellular ligand-binding domain. Segments S0–S4 comprise the VSD, whereas segments S5 and S6 from all four subunits contribute to the central, K+-selective pore (K+ ions occupying the pore are shown as purple spheres). Each subunit also contributes an intracellular RCK1/RCK2 heterodimer, which assembles into the hetero-octameric gating ring superstructure. The structure shown for domains S1–S6 is from the atomic structure of the KV1.2-2.1 chimera (Protein Data Bank accession no. 2R9R) (Long et al., 2007); S0 was modeled as an ideal α helix. Note its close association with voltage-sensing segments S3 and S4, as recently suggested by Liu et al. (2010). The intracellular domain structures (available from Protein Data Bank accession no. 3NAF) (Wu et al., 2010) were manually docked on the 2R9R structure.