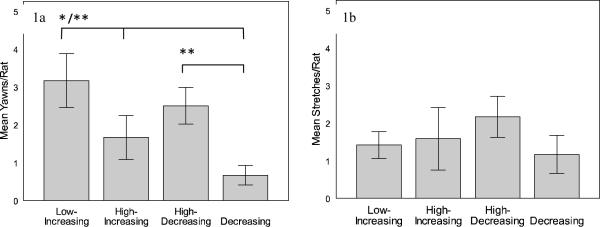
Figure 1.
Behavioral frequencies (mean ± SE) are from a total of 20 minutes in each condition (asterisks indicate significantly higher yawning for that condition, while bars represent pairwise comparisons). Yawning rates differed across the range and direction of ambient temperatures (1a). Yawning occurred more frequently during low-increasing temperatures in comparison to high-increasing and low-decreasing temperatures. In addition, high-decreasing temperatures produced more yawning than low-decreasing temperatures. Unlike yawning, stretching did not differ across temperature variation (1b).
* = significantly different at p < 0.05 level
** = significantly different at p < 0.01 level