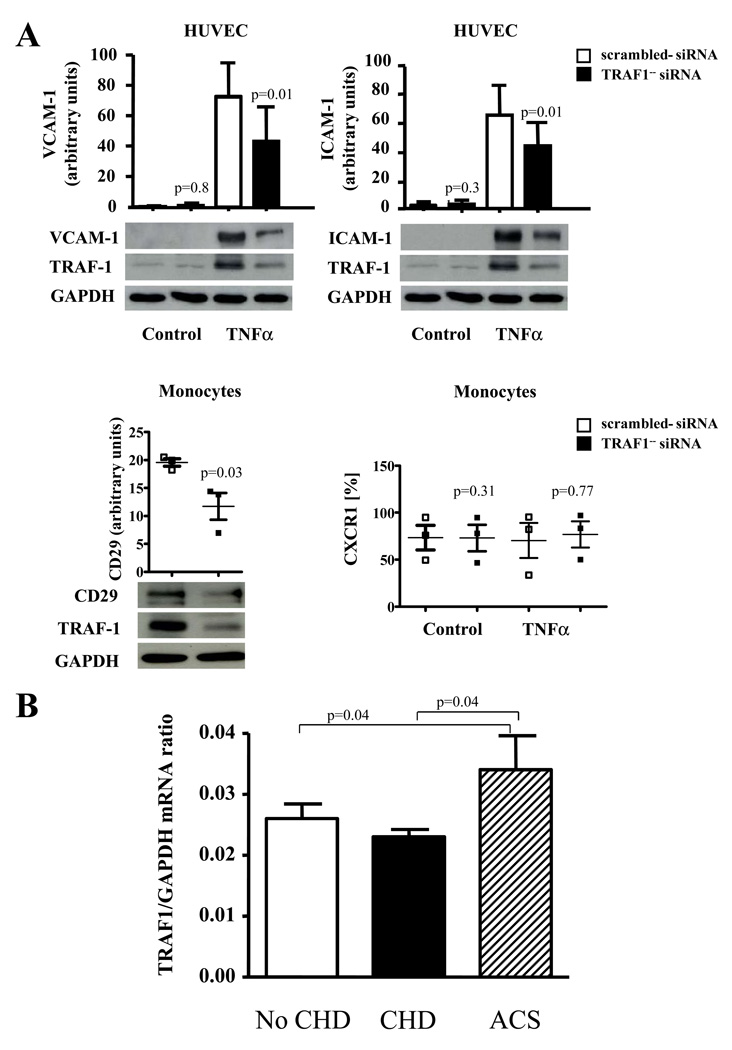
Figure 8. TRAF1-silencing in EC and monocytes limits the expression of adhesion molecules and integrines and TRAF1 mRNA expression increases in acute coronary syndromes in humans.
A. Human umbilical endothelial cells and human monocytes were transfected with TRAF1-specific- or scrambled siRNA. Cells were stimulated with TNFα (20ng/ml) for 24h and expression levels of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 (N=4 each) in endothelial cells, and Integrin beta 1(CD29) and CXCR1 (N=3 each) in human monocytes analyzed by Western blotting. Densitometric results adjusted for GAPDH are presented as mean±SEM on top and as grouped scatter blot, representative blots below.
B. 325 patients undergoing coronary angiography were divided into the three groups: no coronary heart disease (No CHD), stable coronary heart disease (CHD), and acute coronary syndromes (ACS). TRAF1 and GAPDH mRNA was analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR in total blood RNA. Spearman correlation coefficients for continuous variables were used to assess univariate correlations of TRAF1 levels with all variables. Results are presented as mean±standard error computed from the average measurements obtained from each group.