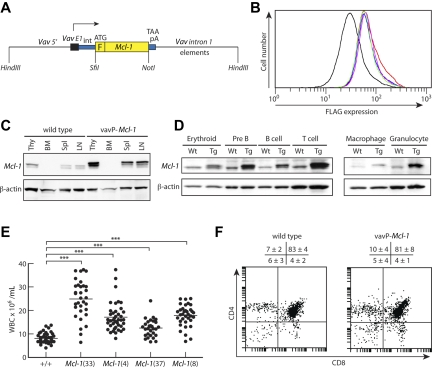
Figure 1.
Pan-hematopoietic transgene expression in vavP-Mcl-1 transgenic mice. (A) Transgenic vector containing a mouse Mcl-1 cDNA linked to an N-terminal FLAG tag, F, flanked by promoter/enhancer elements from the vav gene.29 (B) Flow cytometric analysis of thymocytes after intracellular staining with FLAG-specific antibody to detect level of transgene expression. Each line represents one mouse. Mean fluorescence intensities are 39.6 for WT (black), 71.8 for Mcl-1(37) (green), 77.6 for Mcl-1(8) (magenta), 77.7 for Mcl-1(4) (blue), and 84.3 for Mcl-1(33) (red). (C) Western blot analysis of tissue lysates from thymus (Thy), BM, spleen (Spl), and LN from a WT (left) or vavP-Mcl-1(33) mouse (right) showing transgenic and endogenous Mcl-1 protein. (D) Western blot analysis of purified cells from WT (Wt) or Mcl-1(33) (Tg) mice: erythroid (Ter 119+ BM cells), pre-B (B220+IgM− BM cells), B (B220+ LN cells), T (Thy1+ LN cells), macrophage (Mac1+Gr1− BM cells), and granulocyte (Mac1+Gr1+ BM cells). (E) Peripheral white blood cell count for Mcl-1 transgenic mice and their WT siblings at 6 to 8 weeks of age. Bar represents mean: 8.1 × 106/mL for WT (49 mice), 24.9 for Mcl-1(33) (32 mice), 17.15 for Mcl-1(4) (41 mice), 12.5 for Mcl-1(37) (29 mice), and 17.8 for Mcl-1(8) (35 mice). All transgenic lines have significantly higher white blood cell count than WT (***P < .001). (F) Representative dot plots of stained thymocytes from WT or Mcl-1(33) transgenic mice showing percentages of CD4−CD8−, CD4+CD8+, CD4+CD8−, and CD4−CD8+ cells. Data are mean ± SD; n = 9 WT and 6 transgenic mice.