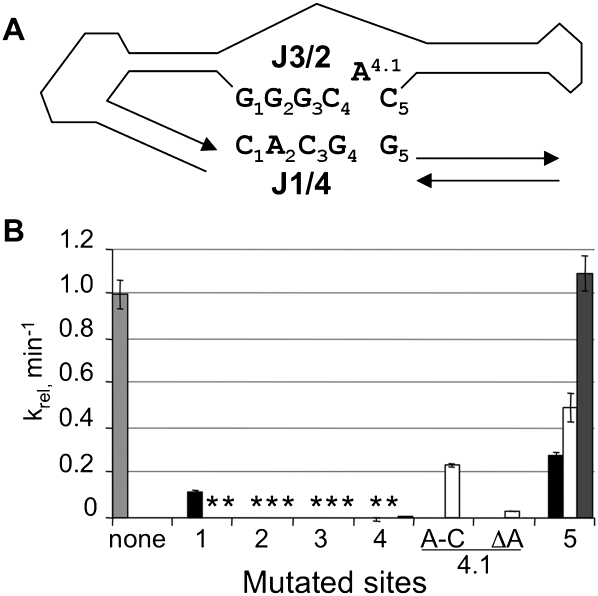
FIGURE 5.
Potential tertiary interactions in Kin.46. (A) Base numbering of nucleotides in J3/2 and J1/4. The rest of the ribozyme is shown schematically. (B) Activities of mutated ribozymes carrying mutations at the positions indicated, normalized to the activity of the original Kin.46, in the presence of EO0. For each mutant, the indicated position was changed to its Watson-Crick complement (A changed to U; G changed to C, etc.). The light gray bar, representing the original Kin.46 ribozyme, indicates no changes; the black bars, mutations within J1/4 only; white bars, mutations within J3/2 only; the dark gray bar, compensatory mutations within both strands, as detailed in the text. A-C is an A-to-C mutation at position 4.1; ΔA is a deletion of this same nucleotide. Where no bars are visible (*), measured activity was >1000-fold reduced relative to activated Kin.46.