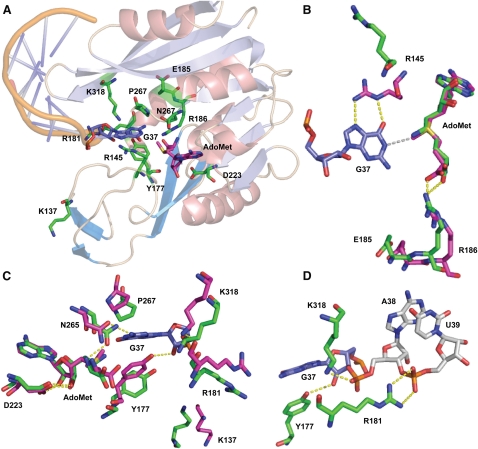
FIGURE 3.
Structure of the M. jannaschii Trm5 active site bound to tRNA and AdoMet. (A) An overall view of the active site, showing all of the residues that have been tested by mutational analysis in this work. (B) Spatial positioning of the catalytic residues R145 and E185 relative to G37 and AdoMet. The position and interactions of the adjacent R186 are also depicted. (C) Detail of the Trm5 active site showing close juxtaposition of G37 N1 with the AdoMet methyl group. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted yellow lines. Key enzyme residues mentioned in the main text are shown in green in the enzyme binary complex with sinefungin, and are shown in red in the enzyme ternary complex with AdoMet and tRNA. (D) Trm5 residues that stabilize the backbone groups of G37 and A38 in the anticodon loop of the ternary complex. Figures are drawn with PyMol (PDB 2YX1) corresponding to Trm5–sinefungin and with PyMol (PDB 2ZZN) corresponding to the Trm5–tRNACys–AdoMet ternary complex (Goto-Ito et al. 2009). H-bonds are shown in yellow dots, while the distance between the N1 position of G37 and the methyl group of AdoMet is shown in gray. Superposition of the two structures in (B), (C), and (D) was done by aligning sinefungin in the binary complex with AdoMet in the ternary complex, with an RSMD of 0.47 Å on the basis of the superposition of α-carbon atoms.