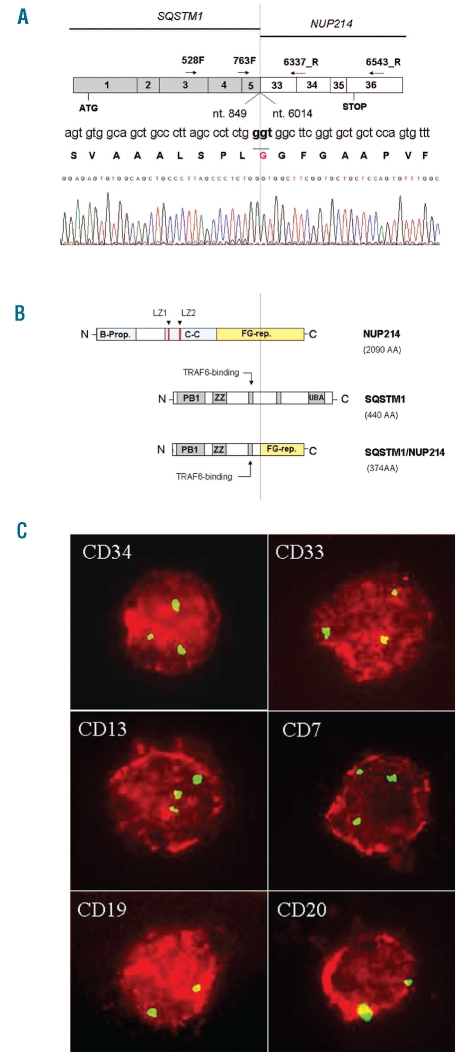
Figure 2.
Molecular characterization of SQSTM1-NUP214 fusion transcript and FICTION experiments. (A) Schema of SQSTM1-NUP214 fusion transcript. SQSTM1 nucleotide 849 (exon 5) is fused in-frame to NUP214 nucleotide 6014 (exon 33). Arrows indicate the primers used in PCR amplification. Dotted line indicates fusion point. Sequence numbers refer to GenBank accession NM_003900.4 for SQSTM1 and NM_005085.2 for NUP214. (B) Schema of NUP214 (2090 AA) (upper), SQSTM1 (440 AA) (middle) and the predicted SQSTM1/NUP214 fusion protein (374 AA) (bottom) which contains PB1, ZZ and TRAF6 binding domain derived from SQSTM1 and 14/44 FG repeats derived from NUP214. The FG repeat region is indicated in yellow. B-prop: Beta propeller, C-C: Coiled-coil, LZ: Leucine-zipper, FG-rep: Phenylalanine-Glycine repeats, PB1: Phox and Bem1p domain, ZZ: Zinc finger, UBA: ubiquitin associated domain. (C) FICTION with monoclonal antibodies against CD34, CD33, CD13, CD7, CD19, CD20. Red staining detects positive intact cells expressing the specific antigen. Green spots indicate FISH signals in the nuclei using a FITC-labeled genomic probe (RP11-544A12) for NUP214. Two green signals indicate normal cells; three signals hallmark NUP214 rearrangement.