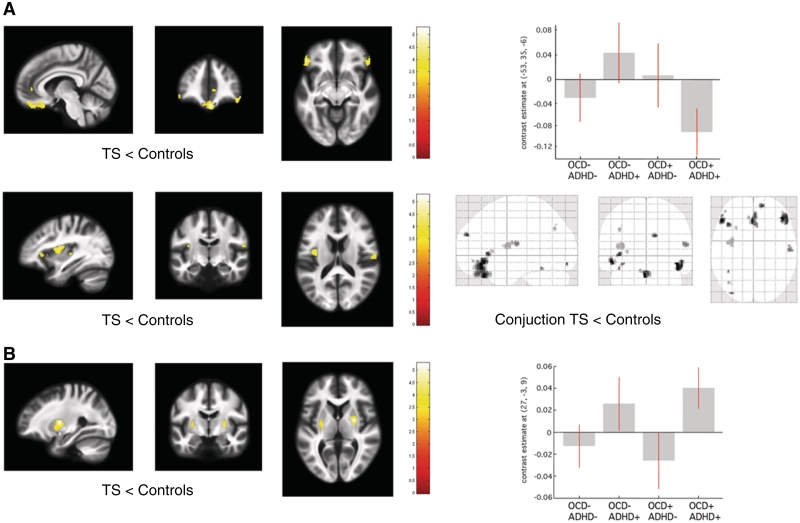
Figure 1.
Statistical parametric maps of significant grey matter volume change in the Tourette syndrome cohort superimposed for presentation purposes at P < 0.001, uncorrected, on T1-weighted image. Right panel: box-plots of regression coefficients (betas) extracted from the voxel of maximum intensity over Tourette syndrome sub-groups depending on the presence (+) or absence (−) of co-morbidity OCD/ADHD (red bars indicating 90% confidence interval); ‘glass brain’ with the result of the conjunction analysis. (A) Grey matter volume decrease in patients with Tourette syndrome (TS) compared with controls. (B) Grey matter volume increase in patients with Tourette syndrome compared with controls. [x, y, z] coordinates refer to the Montreal Neurological Institute space. Colour scales on the right indicate t-values.