Figure 2.
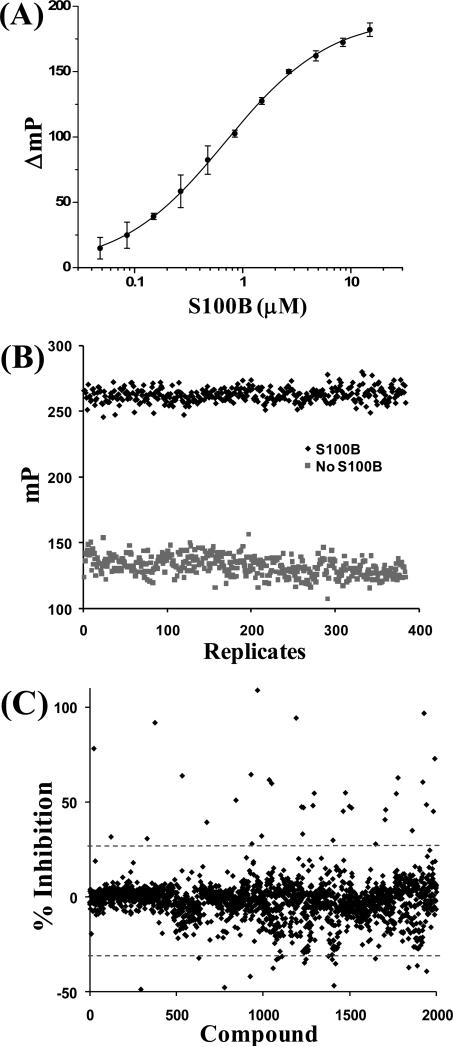
Schematic illustrating the FPCA. The FPCA uses the change in polarization of a TAMRA-labeled peptide derived from residues 265–276 of the actin capping protein CapZ (TAMRA-TRTK) that binds to S100B in the same region as p53 peptide (see Figure 1). In the presence of calcium, S100B binds TAMRA-TRTK causing the peptide to rotate slower, and the polarization values to increase. The addition of compounds that bind the same region displace the peptide, allowing it to rotate freely and decreasing the polarization value. A HTS version of this assay was used to screen for putative inhibitors of S100B, and it is also used to determine the binding affinity (KD) of the compound to S100B (see Table 2). The S100B dimer is shown in blue, the TAMRA-TRTK in red, and the Ca2+ ions are shown as orange spheres.
Abbreviations: FPCA, fluorescence polarization competition assay; high-throughput screening.