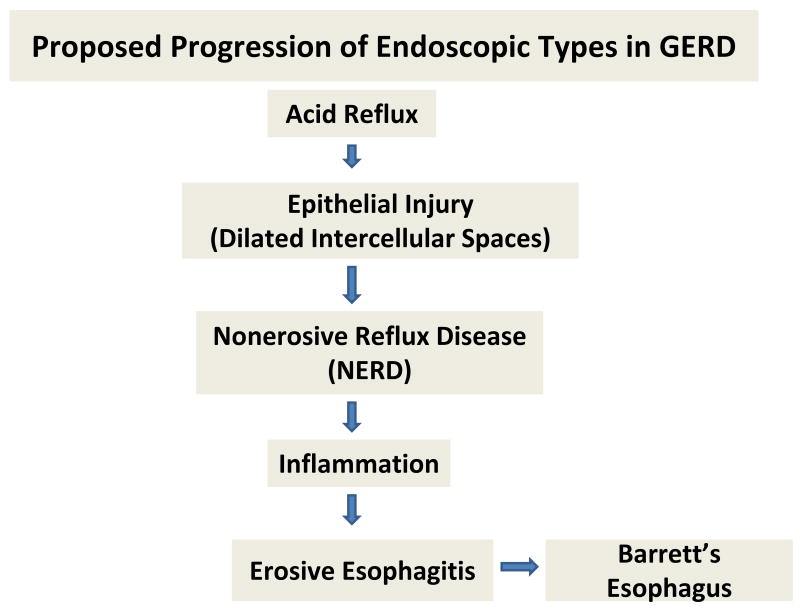
Figure 2.
The diagram depicts a proposed means by which acid injury to esophageal epithelium leads to the three common endoscopic types of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): nonerosive reflux disease (NERD), erosive esophagitis, and Barrett's esophagus. Notably, all three have in common the histopathologic lesion of dilated intercellular spaces within esophageal ‘squamous’ epithelium; and inflammation is shown to be the promoter of progression from NERD to erosive esophagitis. Barrett's esophagus is an aberrant form of repair that occurs in some subjects and this is shown to extend from erosive esophagitis.