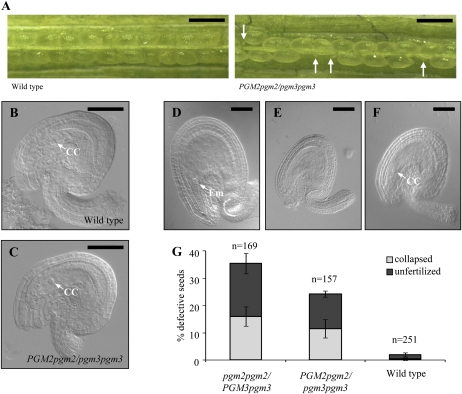
Figure 4.
Seed and ovule development in the wild type compared to PGM2pgm2/pgm3pgm3 and pgm2pgm2/PGM3pgm3 mutants. Results for PGM2pgm2/pgm3pgm3 and pgm2pgm2/PGM3pgm3 mutants were the same. Only PGM2pgm2/pgm3pgm3 is shown. A, Siliques of the wild type and the PGM2pgm2/pgm3pgm3 mutant. White arrows indicate aborted seeds. Bars = 1 mm. B, Representative light microscopy picture of unfertilized ovules of the wild type. CC, Central cell. C, Representative light microscopy picture of unfertilized ovules of the PGM2pgm2/pgm3pgm3 mutant. Ovules from pgm2pgm2/PGM3pgm3 mutants were indistinguishable from the other two genotypes. D to F, Seeds of self-pollinated PGM2pgm2/pgm3pgm3 mutants 3 d after pollination were categorized into normal wild-type-like (D), collapsed (E), and unfertilized (F) seeds. Em, Embryo. pgm2pgm2/PGM3pgm3 mutants showed essentially a comparable distribution into the same categories. In B to F, bars = 50 μm. G, Quantification of the percentage of wild-type-like and defective seeds (as shown in D–F) in the three genotypes. n, Number of seeds counted.