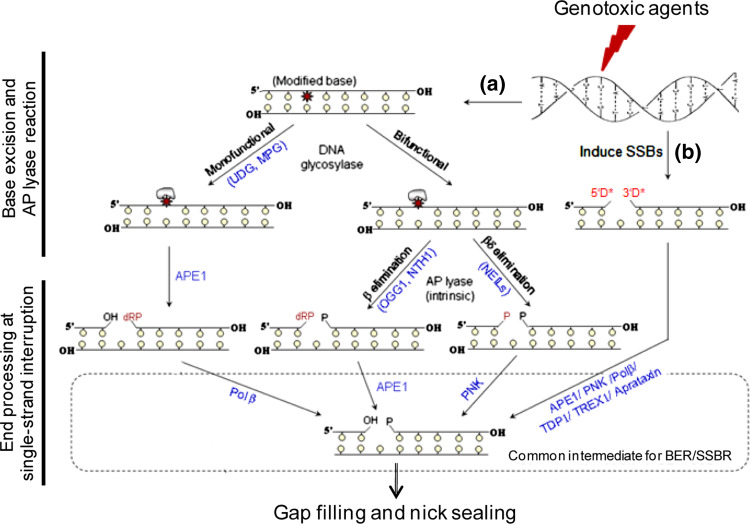
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of base excision (a) and single-strand break (b) repair steps in mammalian cells. Monofunctional DNA glycosylases (UDG, MPG) excise alkylated and modified bases from DNA to generate AP sites that are then cleaved by APE1. The 5′ blocking group at the break site is removed by Polβ to generate a single-nucleotide gap that is filled in by Polβ (and sealed by DNA ligase IIIα). Oxidized bases are excised by OGG1/NTH1 and NEILs which also cleave the DNA strand to generate 3′ blocking groups. DNA is directly cleaved by ROS/radiation and topoisomerases to generate 3′ or 5′ blocking groups (3′D* and 5′D*) which are removed by several end cleaning enzymes. Other details are described in the text