Figure 1.
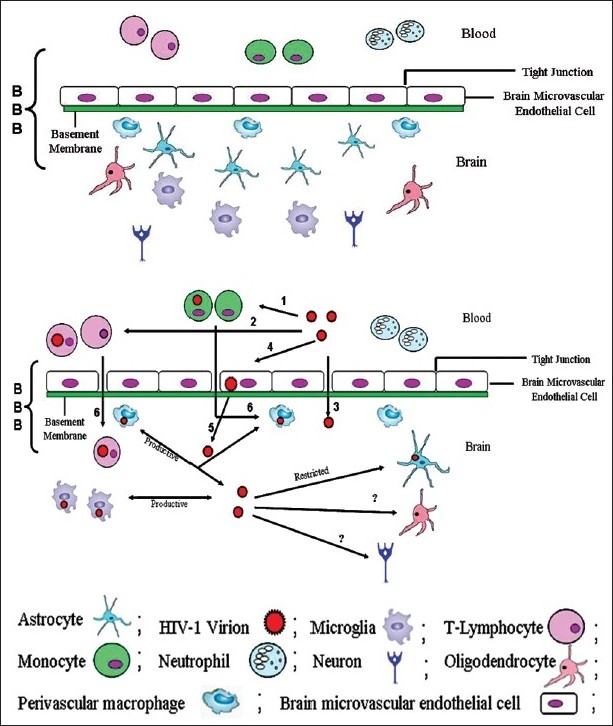
Neuroinvasion of HIV-1: the figure depicts cellular components of blood–brain barrier (BBB). 1a) A normal BBB is represented here. It contains different cell types, viz., astrocytes, microglia, microvascular endothelial cells, oligodendrocytes, perivascular macrophages, etc. 1b) This figure is a graphical representation of various means for HIV entry into CNS including “Trojan horse hypothesis”. (1 and 2) HIV infection to monocytes and T-lymphocytes in peripheral blood circulation. Upon HIV infection there can be breaches in BBB where (3) HIV may directly enter into brain via opening in tight junction, (4 & 5) HIV entry into the brain by transcytosis phenomenon, (6) HIV-infected monocytes and T-lymphocytes acts as carrier for HIV infections to the brain, and (?) mechanism of HIV infection to neurons and oligodendrocytes is still questionable
