Figure 2.
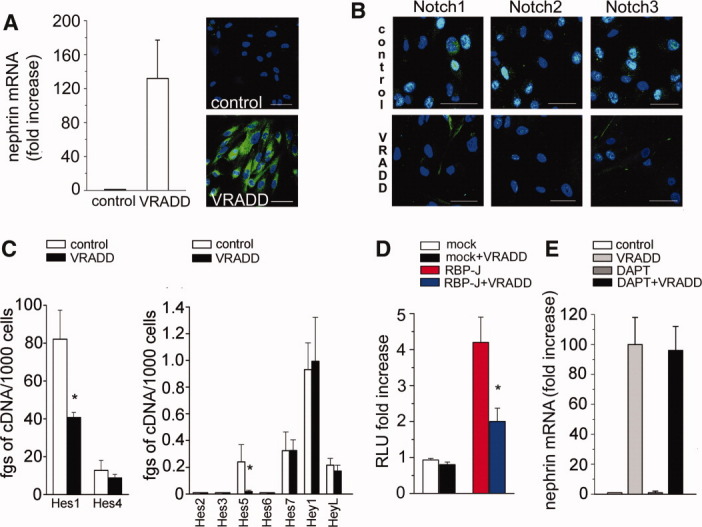
Notch pathway downregulation during human renal progenitors differentiation toward the podocyte lineage. (A): Left: Nephrin mRNA levels in renal progenitors before and after culture in VRADD medium, as assessed by real time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Results are expressed as mean ± SEM of fold level increase for nephrin mRNA before (control) and after 48 hours of culture in VRADD medium obtained in four separate experiments. Right: Nephrin protein expression (green) in renal progenitors as assessed by confocal microscopy before (top) and after (bottom) 48 hours of culture in VRADD medium. Topro-3 (blue) counterstains nuclei. One representative of four independent experiments is shown. Scale bar = 50 μm. (B): Notch1, Notch2, and Notch3 protein expression (green) as assessed by confocal microscopy in control cells (top) and after 48 hours of culture in VRADD medium (bottom). Topro-3 (blue) counterstains nuclei. One representative of eight independent experiments is shown. Scale bar = 50 μm. (C): Notch-target genes mRNA levels in renal progenitors before (control) and after 48 hours of culture in VRADD medium, as assessed by real time quantitative RT-PCR. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM obtained in six separate experiments. (*, p < .05). (D): Downregulation of the Notch pathway activity in renal progenitors following differentiation toward the podocyte lineage, as assessed by infection with a reporter vector for the RBP-J transcriptional response element. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM fold increase of luciferase activity in comparison with renal progenitors infected with the empty expression vector as obtained in eight independent experiments. (*, p < .05). (E): Effect of DAPT treatment on the increase of mRNA level for nephrin in renal progenitors before (control) and after 48 hours of culture in VRADD medium. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM of fold level increase obtained in four separate experiments. Abbreviations: DAPT, N-[N-(3,5-Difluorophenacetyl)-L-alanyl]-S-phenylglycine t-butyl ester; fgs, femtograms; RBP-J, Recombination signal-binding protein-J; RLU, relative luminescence unit; VRADD, vitamin D3, retinoic acid and dexamethasone-supplemented DMEM/F12.
