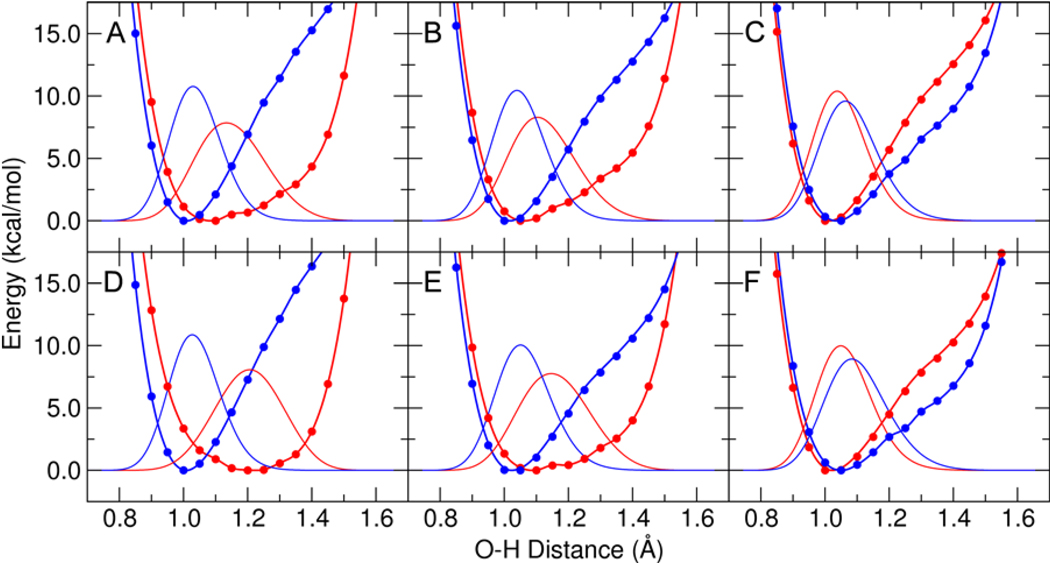
Figure 10.
Proton potential energy curves and corresponding proton vibrational wavefunctions for 3,4,5-trifluorophenolate in (A), (B), and (C) and for phenolate in (D), (E), and (F). The proton potentials were determined from QM/MM calculations of the phenolate bound to pKSI D40N in (A) and (D), with the additional Y32F mutation in (B) and (E), and with the additional Y32F/Y57F mutation in (C) and (F). The single point QM/MM energies are depicted with points, the fits are depicted with thick lines, and the proton vibrational wavefunctions are depicted with thin lines. Results are shown in red for the Tyr16-phenolate hydrogen bond and in blue for the Asp103-phenolate hydrogen bond. All calculations included Tyr16, Asp103, Asp40Asn, residue 32, residue 57, and the phenolate in the QM region.