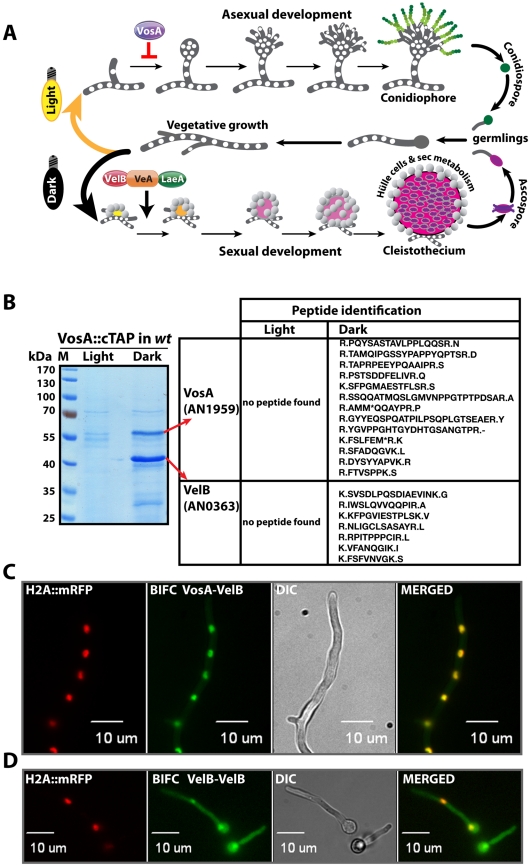
Figure 1. Life cycle of Aspergillus nidulans and identification of the VosA-associated proteins by tandem affinity purification.
(A) Aspergillus nidulans can grow as a filament (vegetative growth). Light favors asexual development and results in asexual spores (conidiospores) produced by conidiophores. Asexual development is repressed by VosA protein. Darkness favors sexual development and requires the trimeric VelB-VeA-LaeA complex. This leads to fruiting bodies (cleistothecia) nursed by Hülle cells. Meiotically produced sexual spores (ascospores) are formed within the fruiting bodies. White round dots indicate the haploid nuclei of the fungus. (B) SDS-polyacrylamide (10%) gel electrophoresis of TAP enrichment for VosA stained with brilliant blue G. Polypeptides identified from the bands of affinity purification from the light and dark grown cultures are shown (Table S4). (C) Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BIFC) in vegetative hyphae with enriched nuclear interaction of the VosA-VelB heterodimer. The N-terminal half of the enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (EYFP) fused to the N-terminus of the VosA protein (N-EYFP::VosA) interacts with the C-terminal half of EYFP fused to VelB (C-EYFP::VelB) in vivo. Histone 2A monomeric red fluorescent protein fusion (H2A::mRFP) visualizes the nuclei. (D) BIFC of the VelB-VelB homodimer formation in the cytoplasm and nuclei. N-EYFP::VelB interacts with C-EYFP::VelB.