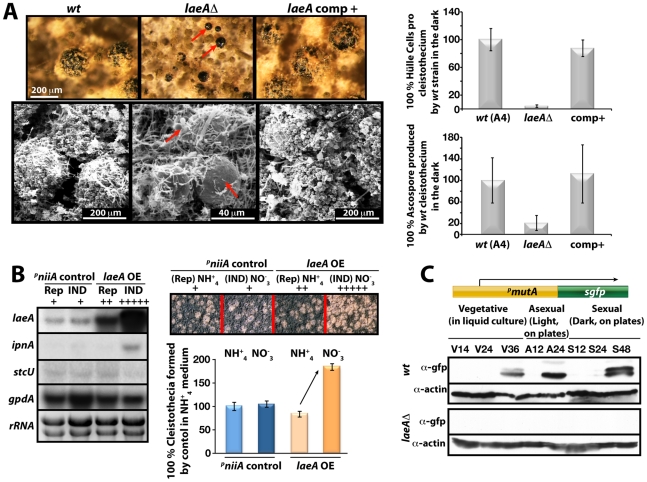
Figure 7. LaeA-dependent Hülle cell formation.
(A) Stereo- (top) and scanning electron (SEM) micrographs of wild type (wt), laeAΔ, and laeA complemented strains and quantification of Hülle cells and ascospores per cleistothecium in the dark. Small cleistothecia produced by laeAΔ strain without Hülle cells are indicated by red arrows. Hülle cells and ascospores were counted from 10 different cleistothecia of wt, laeAΔ and laeA complemented strains photographed by SEM. Vertical bars represent standard deviations. Relative values (%) to the numbers of Hülle cells (100–120) or ascospores (2×105) per cleistothecium in wild type are presented. (B) Overproduction of LaeA in veA+ strain increases sexual fruiting body formation in the dark. Growth of wild type (wt) containing an empty niiA promoter plasmid (control), and pniiA::laeA strains. Repressive (5 mM ammonium tartrate) and inducive (10 mM sodium nitrate) conditions were used to confer different levels of the niiA promoter activity. Fruiting body formation of wild type is not affected by these nitrogen sources. The laeA transcript levels were monitored by Northern blot analyses in comparison to ipnA, stcU. gpdA levels and ethidium bromide stained rRNA were used as controls; 20 µg RNA were applied in each lane. Spores (5×103) were point-inoculated on solid medium and grown at 37°C for 5 days on plates in the dark and cleistothecia were quantified as described [49]. (C) Western blot analysis of Hülle cell specific activity. pmutA::sgfp is specifically expressed in Hülle cells. wt and laeAΔ strains carrying the reporter were grown for indicated time points at 37°C and Western blot with α-gfp, and α-actin as control were performed. 80 µg total protein was applied.