Table 1.
One-pot synthesis of allylic alcohols using an organocatalytic epoxidation-Wharton sequence 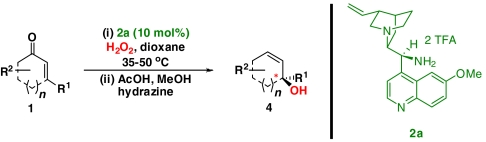
| Entry | Enone (1) | Product (4) | Yield (%)* | ee (%)† | ||
| 1 | 1a | 4a | 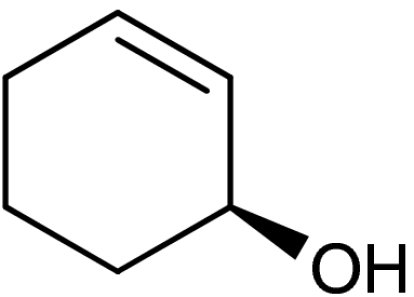 |
50 (32)§ | 93 (93)§ | |
| 2 | 1b | 4b | 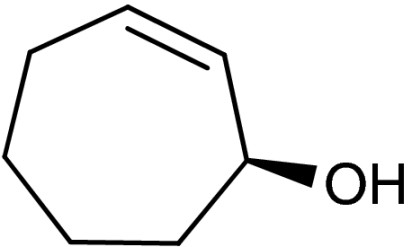 |
45 | 92 | |
| 3 | 1c | 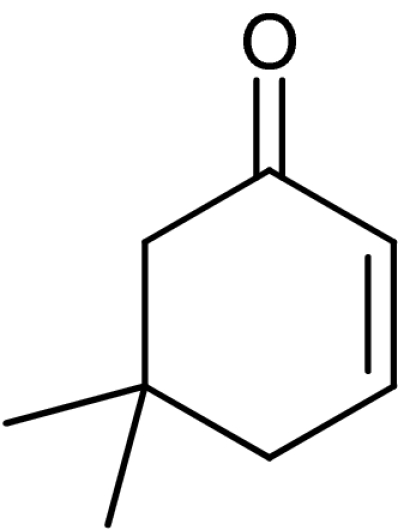 |
4c | 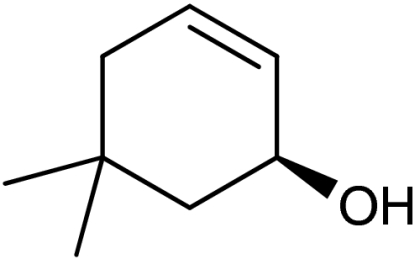 |
58 | 87 |
| 4 | 1d | 4d | 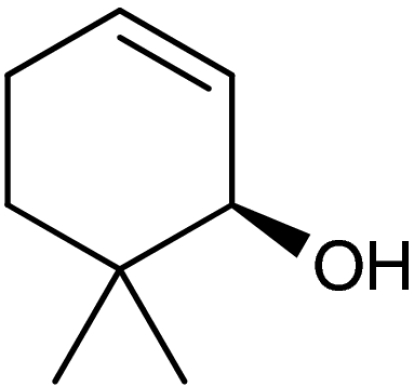 |
47 | 94 | |
| 5 | 1e | 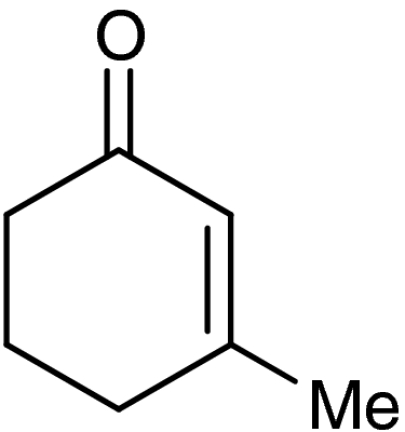 |
4e | 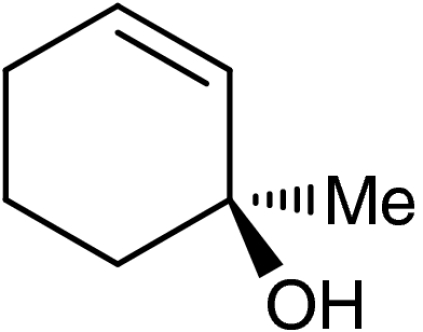 |
40 (35)§ | 94 (94)§ |
| 6 | 1f | 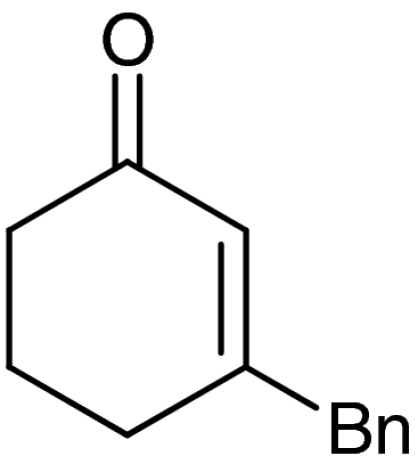 |
4f | 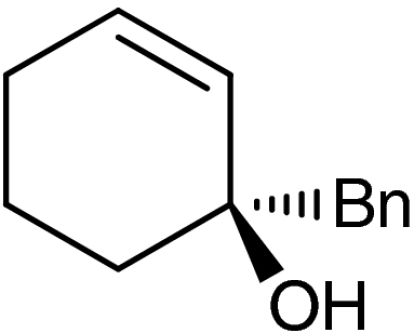 |
40 | 98 |
| 7 | 1g | 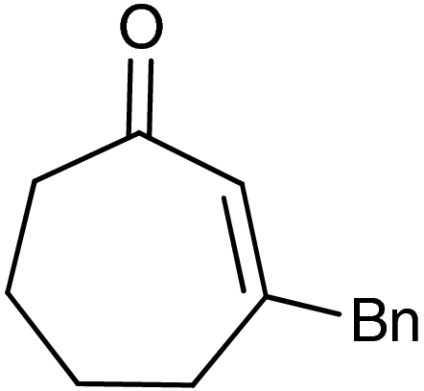 |
4g | 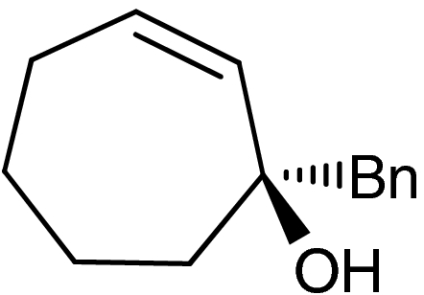 |
45 | 99 |
| 8‡ | 1g | 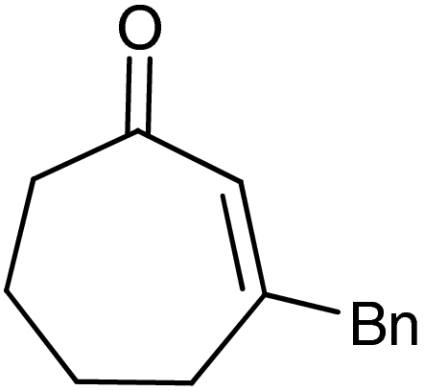 |
ent-4g | 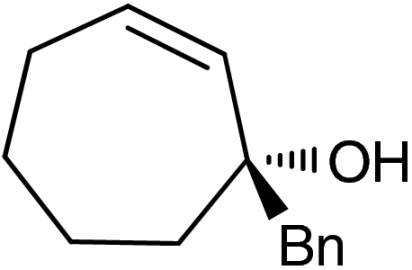 |
42 | 96 |
| 9 | 1h | 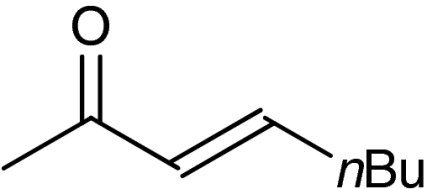 |
4h | 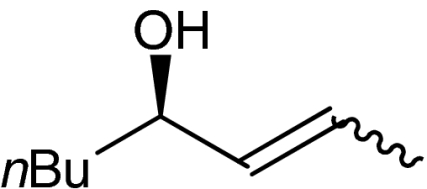 |
54 | 96 |
*Yields of isolated products.
†Determined by chiral stationary phase GC or HPLC.
‡The quasienantiomer of the catalyst is used (2b, see Scheme 5).
§Results for the sequence performed in two separate steps.
