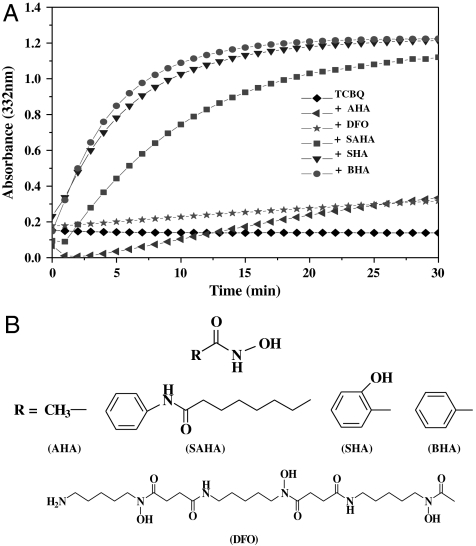
Fig. 1.
(A) The hydrolysis of TCBQ to DDBQ was markedly enhanced by BHA and other hydroxamic acids. All incubation mixtures contained 0.2 mM hydroxamic acids in phosphate buffer (10 mM, pH 7.0) at room temperature. The reactions were initiated by the addition of TCBQ (0.05 mM), followed by rapid mixing. DDBQ formation was monitored at 332 nm for 30 min. AHA: acetohydroxamic acid; DFO: deferoxamine; SAHA: suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid; and SHA: salicylhydroxamic acid. Each point represents the mean of two separate experiments with the SD less than 5%. (B) The chemical structures of hydroxamic acids used in this study.