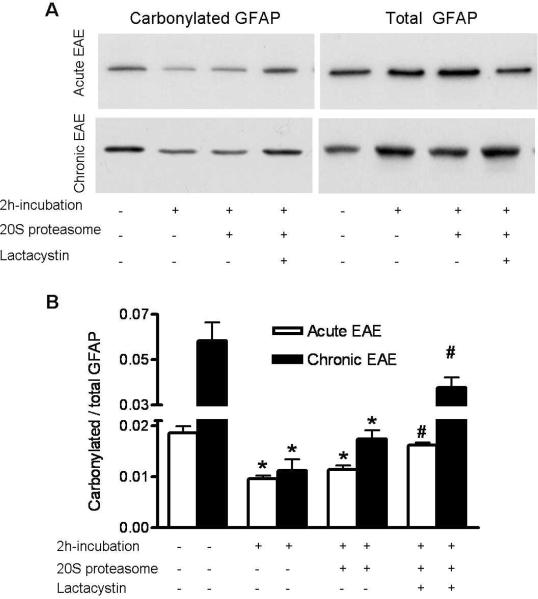
Fig. 8.
Carbonylated GFAP from acute and chronic EAE animals are sensitive to proteasomal degradation in a cell-free system. Cerebellum homogenates from acute and chronic EAE mice (200 μg protein) were incubated with 0.5 μg of 20S proteasome (Sigma) in the absence or presence of 2μg clasto-lactacystin-β-lactone (Enzo Life Sciences). After 2 h, carbonylated proteins were isolated using the pull-down procedure described in “Materials and Methods”. A representative western blot of the total and bound fractions developed with an antibody against GFAP is shown in panel A. Densitometric scans were obtained to calculate the proportion of carbonylated GFAP in the various conditions (Panel B). The 20S chymotrypsin-like activity in the homogenates increased ~12-fold upon addition of 20S proteasome and was reduced by ~90% in the presence of clasto-lactacystin-β-lactone. Values represent the mean ± SEM of 4 experiments. *Significantly different (p<0.05) from non-incubated condition; #Significantly different (p<005) from the 20S proteasome-treated condition.