Figure 3.
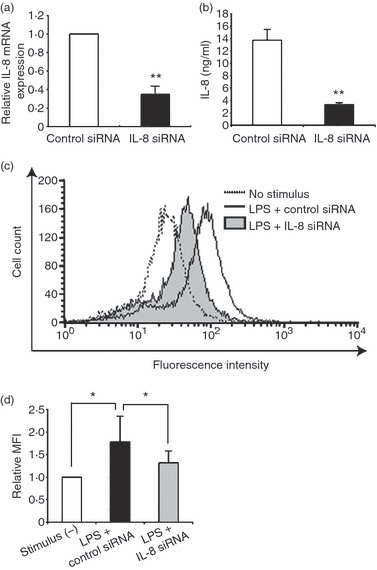
Effect of interleukin-8 (IL-8) knockdown on reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) -stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). (a) The relative messenger RNA expression of IL-8 in LPS-stimulated HUVECs treated with IL-8 small interfering (si) RNA as determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction. The expression level is shown relative to that in LPS-stimulated HUVECs treated with control siRNA. The data represent mean values ± SD (n = 3, **P < 0·01, Student's t-test). (b) IL-8 protein expression in LPS-stimulated HUVECs treated with IL-8 siRNA by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The data represent mean values ± SD (n = 4, **P < 0·01, Student's t-test). (c) Representative data of ROS production assessed by flow cytometry using DCFH-DA in LPS-stimulated HUVECs. The cells were treated with IL-8 siRNA or control siRNA. (d) Quantitative analysis of ROS production in LPS-stimulated HUVECs with control siRNA or IL-8 siRNA treatment. The data represent mean values ± SD (n = 4, *P < 0·05, Student's t-test).
