Figure 4.
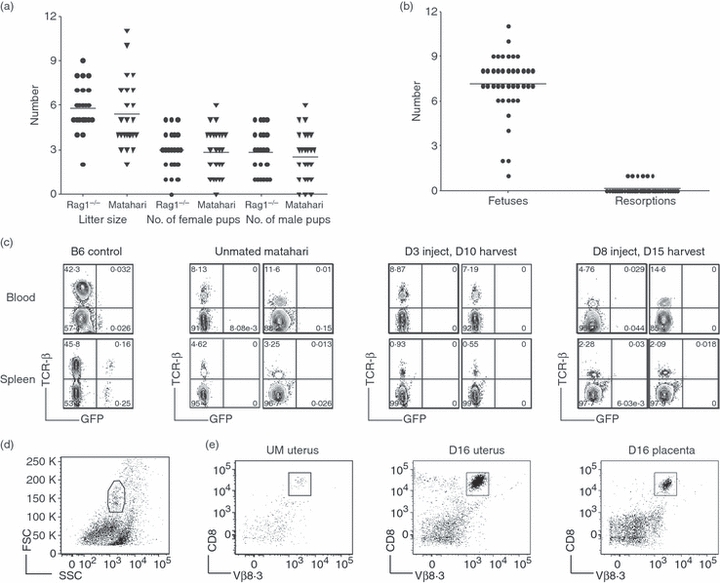
Anti-HY Matahari T-cell receptor (TCR) transgenic CD8 T cells are functional during pregnancy with no adverse effects on fetal survival. (a) Litter size and the number of male and female pups on weaning from breeding pairs of anti-HY Matahari TCR transgenic and non-transgenic Rag1−/− mice. (b) The number of fetuses and resorptions from 40 Matahari pregnancies at various gestational days. (c) CD8 T-cell activity was tested by injecting day 3 or 8 pregnant Matahari, unmated Matahari, and B6 control mice with male GFP+ spleen cells. Seven days later the presence of GFP+ cells was determined in the blood (top) and spleen (bottom) by flow cytometry. Non-transgenic B6 mice were used as controls (left most panels). Profiles for two mice from each time-point analysed are shown. Numbers refer to percentage of cells in the lymphocyte gate. (d) Representative flow cytometric gating from a Matahari day 16 uterus. (e) Isolation of CD8+ T cells from the uterus and placenta of Matahari mice. Fetal–placental units were removed and the uteri of four pregnant mice were pooled. Pooled uteri from four unmated mice were run as controls. For each pregnant mouse, two placentas from each uterine horn were pooled together (four in total). CD8 T cells were isolated from enzymatically digested uterus and placenta samples by magnetic antibody cell sorting positive selection and visualized by flow cytometry. CD8+ Vβ8.3+ T cells were purified from unmated uterus (left), day 16 uterus (middle), and day 16 placenta (right).
