Fig. 4.
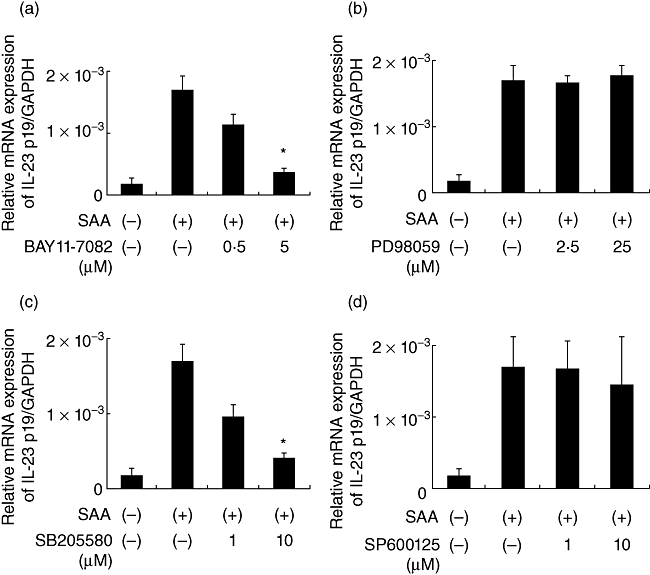
Nuclear factor (NF)-κB and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinease (MAPK) inhibition suppressed interleukin (IL)-23 p19 mRNA expression. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synoviocytes were incubated with vehicle (dimethylsulphoxide, media), BAY11-7082 (a, nuclear factor-κB inhibitor), PD98059 (b, extracellular regulated kinase pathway inhibitor), SB203580 (c, p38 inhibitor) and SP600125 (d, c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor) for 1 h. Cells were then stimulated with 5 µg/ml of serum amyloid A (SAA) for 6 h and interleukin (IL)-23 p19 and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase mRNA expression was determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Data are the means of two different RA synoviocytes run in triplicate ± standard error of the mean. *P < 0·0001 compared to SAA-treated RA synoviocytes.
