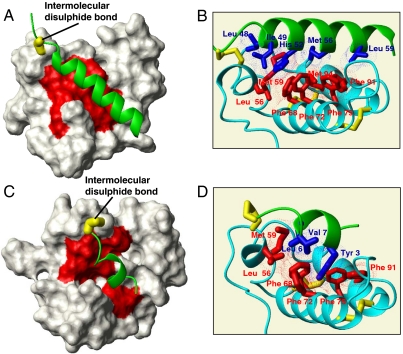
Fig. 2.
Structural characterization of substrate-Mia40 covalent adducts. (A) The solution structure of the Cox17–Mia40 complex: The Mia40-induced α-helix in Cox17 is in green, the NHs chemical shift variations of Mia40 residues upon complex formation are mapped in red, and the intermolecular disulfide bond is in yellow. (B) Hydrophobic residues involved in the protein–protein recognition between Cox17 (in green) and Mia40 (in cyano) are shown in blue and red, respectively. Inter- and intramolecular disulfide bonds are in yellow; van der Waals contacts are shown in blue and red dots. (C) Experimental data-driven docking model of Tim9 peptide–Mia40 complex: The Mia40-induced α-helix in Tim9 peptide is in green, the NHs chemical shift variations of Mia40 residues upon complex formation are mapped in red, and the intermolecular disulfide bond is in yellow. (D) Hydrophobic residues involved in the protein–protein recognition between Tim9 peptide (in green) and Mia40 (in cyano) are shown in blue and red, respectively. Inter- and intramolecular disulfide bonds are also shown in yellow; van der Waals contacts are shown in blue and red dots.