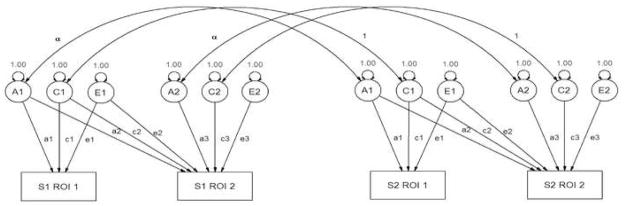
Figure 2.
Example of a path diagram describing the bivariate Cholesky decomposition used to estimate genetic correlations between regions of interest (ROIs). The variance in observed variables (denoted as rectangles) are modeled to be mediated by latent additive genetic (A.), shared environmental (C.) or unique environmental (E.) sources of variance (circles) with latent variances standardized to unity. In this example, two related family members (S1 and S2) are shown. For families with more than two individuals, this model is easily expanded, with families of size k generating (2k)2 informative variance/covariance relationships. Subjects without family members in the present study are not genetically informative, but provide useful information for the estimation of total ROI variances as well as the within-person phenotypic covariance.