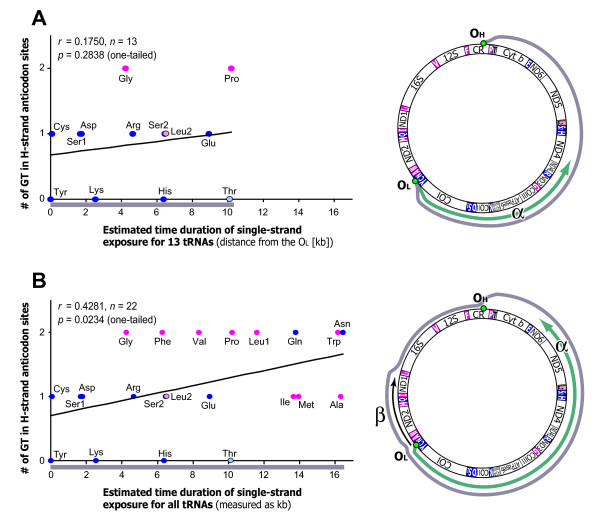
Figure 5.
Correlation between the number of guanine (G) and thymine (T) in 1st and 2nd anticodon positions of tRNA loci and expected time duration of single-strand exposure during mtDNA replication. The analysis is based on a human mt-genome. Data points for the tRNA genes that specify hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acids are colored magenta and blue, respectively; exceptionally, tRNA-Leu (CUN) and tRNA-Thr are shown in light pink and light blue, respectively. (A) Analysis for tRNA genes located between the OL and OH along the direction of L-strand replication (tRNA-Cys, -Tyr, -Ser1, -Asp, -Lys, -Gly, -Arg, -His, -Ser2, -Leu2, -Glu, -Thr, and -Pro). The expected time duration of single-strand exposure was measured as distance from the OL along the direction of L-strand replication. This distance is named as α, as depicted in the right part of the panel A. (B) Analysis for all tRNA genes. For the above-mentioned 13 tRNA genes (described in the legend of the panel A), the duration of single-strand exposure was measured as α. For the other 9 tRNA genes (tRNA-Asn, -Ala, -Trp, -Met, -Gln, -Ile, -Leu1, -Val, and -Phe), the duration of single-strand exposure was estimated as (α - β), where β is distance from the OL along the opposite direction of L-strand replication. This is because, among those 9 tRNA loci, the tRNAs located more distant from the OL along the opposite direction of L-strand replication remain in double-stranded DNA for a longer time based on the displacement model of mtDNA replication [26].