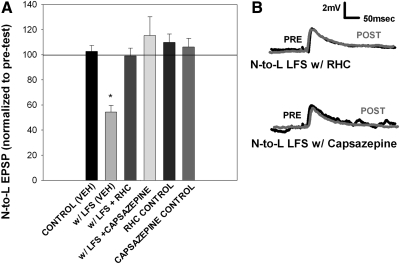
Fig. 3.
Heterosynaptic LTD is mediated by endocannabinoids and a transient potential receptor vanilloid (TRPV)-like receptor. A: bar graph showing the inhibition of heterosynaptic LTD through application of RHC-80267, a 2AG synthesis blocker, and capsazepine, a selective antagonist of TRPV1 receptors. Data were analyzed through a 1-way ANOVA [F(5,20) = 13.39; P < 0.01]. Bath application of 60 μM RHC (n = 4) or 10 μM capsazepine (n = 4) significantly blocked the heterosynaptic LTD observed with vehicle LFS [w/LFS (VEH)]. Post hoc Newman-Keuls tests detected a significant difference between veh LFS vs. veh control (*P < 0.05), vehicle LFS vs. LFS with RHC (*P < 0.05), vehicle LFS vs. LFS with capsazepine (*P < 0.05). There was no change in EPSP amplitude with RHC application alone (n = 3) or capsazepine application alone (n = 3), indicating that the drug itself did not have an effect. B, top: traces of the N-to-L synapse with RHC during LFS. Pretest traces (black line) show no changes compared with posttest traces (gray line) taken after stimulation. Bottom: traces of the N-to-L synapse with capsazepine during LFS. Pretest traces (black line) show no changes compared with posttest traces (gray line), indicating that capsazepine blocked heterosynaptic LTD.