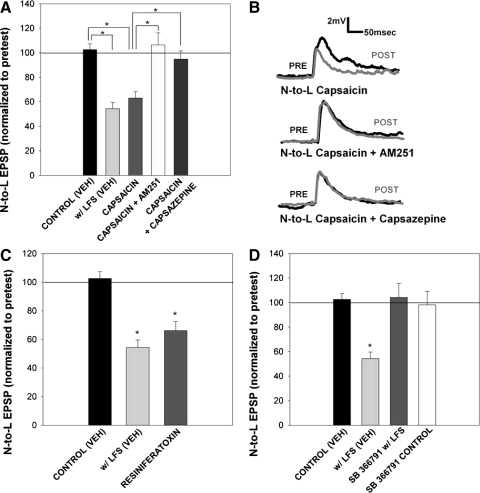
Fig. 5.
Capsaicin and resiniferatoxin mimicked LFS-induced LTD and was blocked by inhibitors of endocannabinoid and TRPV1 receptors. A: bar graph comparing the effects on synaptic transmission following treatment with either vehicle [control (VEH)], LFS in vehicle [w/LFS (VEH)], capsaicin alone (capsaicin, n = 12), capsaicin with 10 μM AM251 (capsaicin + AM251, n = 4), and capsaicin with 10 μM capsazepine (capsaicin + capsazepine, n = 5). One-way ANOVA [F(4,29) = 13.16; P < 0.01] detected a significant effect of treatment group. Newman-Keuls post hoc analysis detected a significant difference between the control (VEH) and w/LFS (VEH) groups (P < 0.05*) and between the capsaicin and control (VEH; P < 0.05*), capsaicin + AM251 (P < 0.05*), and capsaicin + capsazepine (P < 0.05*) groups. B, top: traces of the N-to-L synapse in the presence of 10 μM capsaicin. Baseline pretest traces (black line) show the EPSP amplitude before capsaicin application, while posttest traces (gray line) show a EPSP amplitude after treatment. Middle: traces of the N-to-L synapse in the presence of 10 μM capsaicin with 10 μM AM251. Posttest EPSP traces show no change from pretest EPSP traces if AM251 is applied with capsaicin, indicating that AM251 binds to TRPV receptors. Bottom: traces of the N-to-L synapse in the presence of 10 μM capsaicin and 10 μM capsazepine. Similar to AM251 traces, posttest EPSP amplitude did not differ from pretest EPSP amplitude if capsazepine is applied with capsaicin. C: bar graph comparing the effects on synaptic transmission following treatment with either vehicle [control (VEH)], LFS in vehicle [w/LFS (VEH)], and resiniferatoxin (n = 5). One-way ANOVA detected a significant effect of the resiniferatoxin treatment [F(2,14) = 20.73; P < 0.01]. Post hoc analysis using Newman-Keuls detected a significant difference between the control (VEH) group and w/LFS (VEH) group (*P < 0.05). Post hoc analysis also detected a significant difference between the control (VEH) group and the resiniferatoxin group (*P < 0.05). D: bar graph representing the effect of SB 366791 treatment on heterosynaptic LTD with vehicle [control (VEH)], LFS in vehicle [w/LFS (VEH)], LFS in the presence of SB 366791 (SB 366791 w/LFS; n = 5), and drug treatment control (SB 366791 control, n = 5). One-way ANOVA analysis indicated a significant main effect of the treatment group [F(3,18) = 9.68, P < 0.01]. Newman-Keuls post hoc analyses detected a significance difference between the vehicle LFS group with control (VEH; *P < 0.05) group and SB 366791 w/ LFS (*P < 0.05) group. Drug treatment alone (SB 366791 control) did not have any effect.