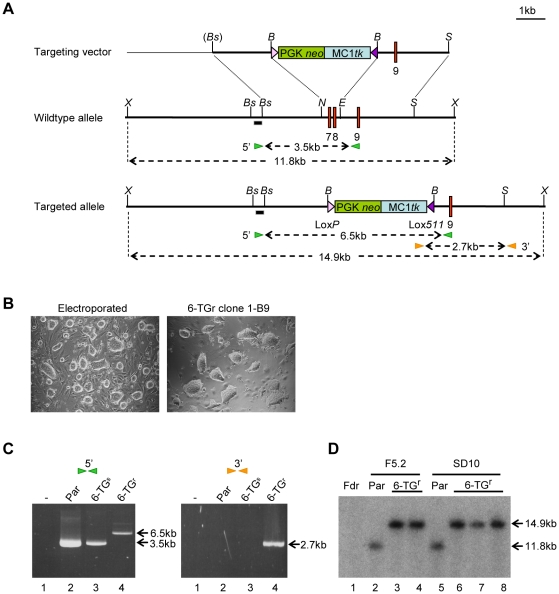
Figure 1. Targeting of the hprt gene in rat embryonic stem cells.
(A) Structure of the HPRT targeting vector (top), the wild-type hprt allele (middle) and targeted allele (bottom), resulting from replacement recombination at the dotted lines. The null allele was created by substitution of exons 7 and 8 with a PGKneo/MC1tk selection cassette (green and blue boxes). Exons are depicted by red boxes, non-exon–containing chromosomal, and cloned, genomic DNA sequence is shown by a thick black line and pBluescript plasmid sequence by a thin black line. Restriction enzyme sites BamHI (B) BstBI (Bs), EcoRV (E), NdeI (N), SacI (S) and XbaI (X) are indicated. Oligonucleotide pairs (green and orange arrowheads) and 5′ probe sequence (hashed box), consisting of sequence homologous and external to the homology arms, were used for PCR-based and Southern screening respectively. Sizes of expected products are shown by dotted arrows. (B) Brightfield image of electroporated RIF5.2 cells two days post-electroporation and prior to selection (left panel), and of a resultant 6-TG-resistant clone 1-B9 (right panel) (Magnification x100). (C) Confirmation of targeted integration by PCR amplification of (1) water blank, and of genomic DNA from (2) RIF5.2 parental rat ES cell line, (3) 6-TG-sensitive wildtype clone and (4) 6-TG-resistant targeted RIF5.2 clone using oligonucleotide pairs shown in (A). (D) Confirmation of targeted integration by Southern blot analysis using 5′ probe shown in panel (A), of XbaI digested genomic DNA from (1) SNL feeder cells, (2) RIF5.2 parental rat ES cell line, (3) RIF5.2-derived 6-TG-resistant clone 1-B9, (4) RIF5.2-derived 6-TG-resistant clone 3-B4, (5) RISD10 parental cell line, (6) RISD10-derived 6-TG-resistant targeted clone 13, (7) RISD10-derived 6-TG-resistant targeted clone 14 and (8) RISD10-derived 6-TG-resistant targeted clone 16.