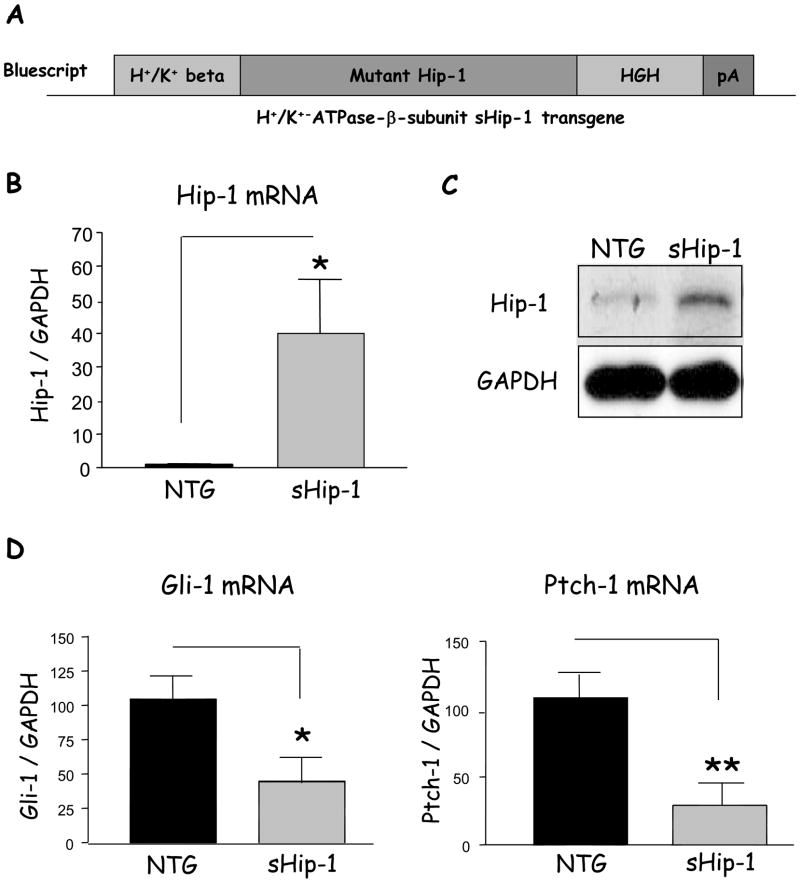
Figure 1. Hip-1 mRNA levels and Shh signaling in the gastric fundus of transgenic mice.
A) The secreted hedgehog interacting protein 1 (sHip-1) transgene, lacking the C-terminal transmembrane domain, was expressed downstream of the H+/K+-ATPase-β subunit promoter, and in frame with the 3′UTR of the human growth hormone (HGH) gene and polyA tail to enhance expression in mammalian cells. The mice expressing the transgene were designated as “sHip-1 mice”. B) Quantitative PCR analysis of Hip-1 mRNA from the sHip-1 mice compared to non-transgenic littermate is shown as the mean +/− SEM for 5 mice per group. C) A representative western blot of Hip-1 protein (85kDa) from a sHip-1 mouse (Founder line 450) compared to non-transgenic littermate is shown. D) Target gene expression of glioma-associated oncogene-1 (Gli-1) and Ptch-1 genes in the sHip-1 fundus versus controls to assay the signaling activity of the Shh pathway (shown is the mean for n = 5 mice per group +/− SEM). P-values are indicated such that * P < 0.05 and ** P < 0.01.