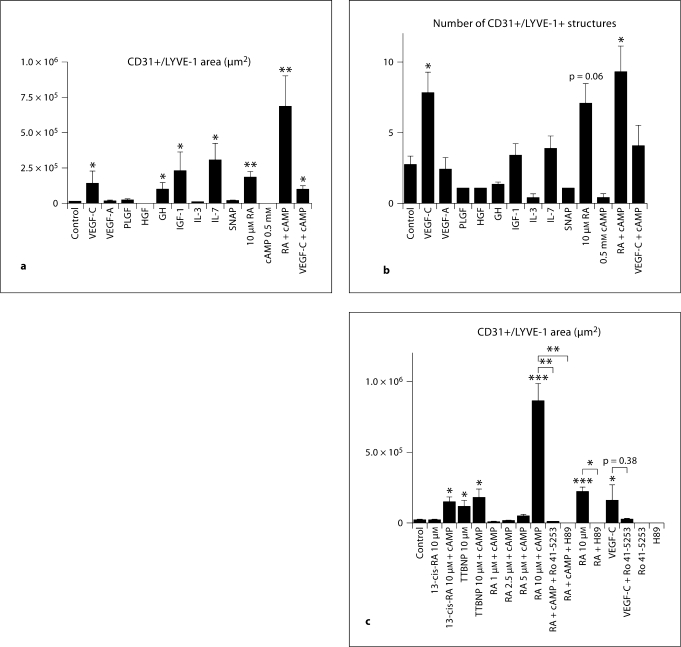
Fig. 1.
The in vitro mouse EB assay reveals that RA and cAMP induce LYVE-1 expression. Mouse EBs were cultured for 14 days and were then incubated with compounds for 4 days. 10 μM all-trans-RA (RA) and RA + 0.5 mM cAMP (RA + cAMP) increased the LYVE-1+ area among CD31+ vessel-like structures (a). VEGF-C, IGF-1, GH and IL-7 also showed a significant induction of LYVE-1 expression (a). 10 μM all-trans-RA + cAMP and VEGF-C induced the formation of several distinct LYVE1+ lymphatic vessel-like structures (b). 13-cis-RA + cAMP and the synthetic retinoid TTBNP (+ cAMP) increased the area of LYVE-1 expression (c). Exposure of EBs to Ro 41-5253, an inhibitor of RAR-α, in combination with RA + cAMP inhibited the expression of LYVE-1 in CD31+ vessel-like structures. H69, an inhibitor of PKA, also inhibited the effects of RA + cAMP. Ro 41-5253 did not significantly inhibit the VEGF-C effect. EBs exposed to the inhibitors alone expressed the same levels of LYVE-1 as controls. Data are expressed as mean values + SEM (n = 5). * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.