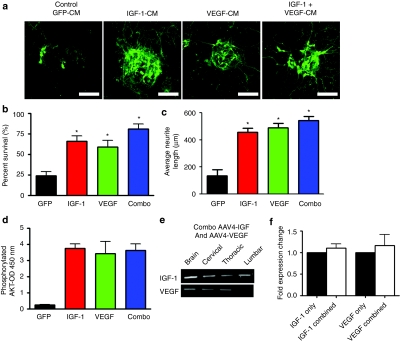
Figure 5.
Combination therapy with both IGF-1 and VEGF-165 does not lead to additive motor neuron protection in vitro. (a) Treatment with IGF-1-conditioned media (CM), VEGF-CM, or IGF-1 and VEGF-CM rescued Hb9:eGFP-GFP+ motor neurons from SOD1G93A astrocyte-mediated toxicity. Original magnification ×20. Bar = 50 µm. (b) Surviving Hb9-GFP+ motor neurons were quantified after 4 days of coculture with SOD1G93A astrocytes. *P < 0.05. (c) Quantification of neurite lengths from Hb9-GFP+ motor neurons in the coculture assay exposed to conditioned medium demonstrating IGF-1 and VEGF and the combination preserved neurite length versus control GFP-CM (*P < 0.05). (d) Levels of phosphorylated Akt were measured in astrocytes by ELISA after 15 minutes of treatment with aCSF, IGF-1, VEGF, or a combination of IGF-1 and VEGF. (e) RT-PCR analysis for viral transgene expression in various regions of the brain and spinal cord after combined delivery of AAV4-IGF-1 and AAV4-VEGF-165. (f) Quantitative-RT-PCR for expression of IGF-1 or VEGF-165 following coadministration versus IGF-1 or VEGF-165 only. AAV4, adeno-associated virus serotype 4; CM, conditioned medium; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; eGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor-1; RT-PCR, reverse transcription-PCR; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.