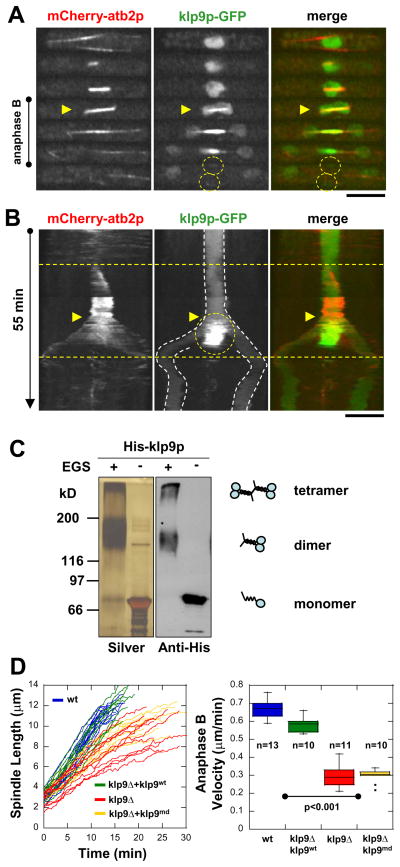
Figure 2. Klp9p may be a tetramer that slides the bipolar spindle apart during anaphase B.
(A) Time-lapsed images of cell expressing mCherry-atb2 (tubulin) and klp9p-GFP. During interphase, prophase, metaphase and anaphase A, klp9p-GFP is located in the nucleoplasm. At the onset of anaphase B (yellow arrow heads), klp9p-GFP goes to the spindle and the spindle midzone. At the end of anaphase B, the spindle breaks down, and klp9p-GFP is transiently at the site of the presumptive contractile ring (yellow dashed circles).
(B) Kymographs of klp9p dynamics throughout the cell cycle. Mitosis in fission yeast lasts ~30 min. Anaphase B (yellow arrow heads) marks a relatively fast spindle elongation rate of ~0.7 μm/min and lasts ~12 min before spindle breakdown. Klp9p-GFP localizes to the spindle at anaphase B onset, and focuses to the spindle midzone throughout anaphase B (yellow dashed circle). Dashed white lines mark the position of the nucleus and divided nuclei. Bar, 5 μm.
(C) EGS cross-linking of recombinant His-klp9p revealed dimers and tetramers.
(D) Comparative plot of spindle length vs. time and box plot of anaphase B spindle elongation velocities of wildtype cells (wt, blue), klp9Δ cells expressing exogenous wildtype klp9 (klp9Δ+klp9wt, green), klp9Δ cells (klp9Δ, red), and klp9Δ cells expressing exogenous klp9 motor dead mutant (klp9md, yellow).