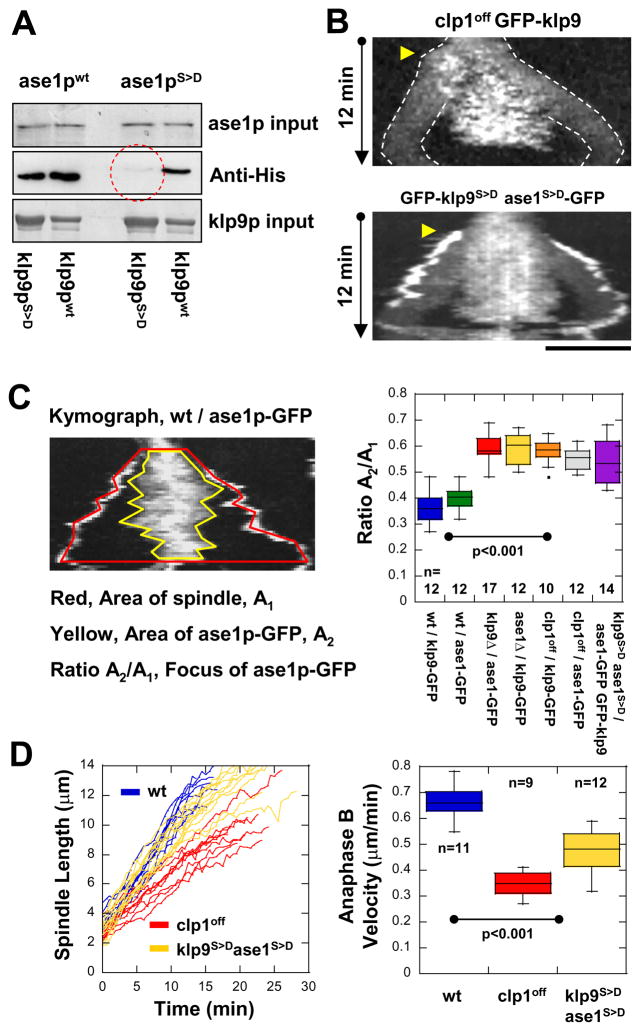
Figure 5. Dephosphorylation of klp9p and ase1p by the phosphatase clp1p (Cdc14) are required for their efficient binding and proper anaphase B spindle elongation.
(A) Pull-down assays of recombinant GST-klp9p and GST-klp9pphosphomimic (GST-klp9pS>D) with recombinant His-ase1p and His-ase1pphosphomimic (His-ase1pS>D). The strongest binding is observed with GST-klp9p and His-ase1p. Bindings are also observed with either GST-klp9p or His-ase1p phosphomimic versions. No binding is observed between GST-klp9pS>D and His-ase1pS>D (red dashed circle).
(B) Kymographs of mutant clp1off cells and double mutant klp9phosphomimicase1phosphomimic (klp9S>Dase1S>D) cells expressing klp9p-GFP during mitosis. Mutant clp1off cells, which have no phosphastase activity, and double mutant klp9S>Dase1S>D cells show GFP-klp9p and ase1p-GFP dispersed to wider regions of the spindle. Bar, 5 μm.
(C) Quantification of klp9p and ase1p focusing at the spindle midzone. Kymograph of anaphase B shows two regions of interest: the area A1 covered by the spindle (red boundary), and the area A2 covered by klp9p-GFP or ase1p-GFP at the midzone (yellow boundary). We defined the ratio of the A2/A1 as the index of focusing. Box plot shows that klp9p-GFP and ase1p-GFP are highly focused at the spindle midzone in wildtype cells. In contrast, phospho-mutants of klp9 and ase1 and clp1off show klp9p-GFP and ase1p-GFP spread out on the spindle.
(D) Comparative plot of spindle length vs. time and box plot of anaphase B spindle elongation velocity of wildtype cells (wt, blue), mutant clp1off cells (clp1off, red), and double mutant klp9 phosphomimicase1phosphomimic cells (klp9S>Dase1S>D, yellow).