Figure 1.
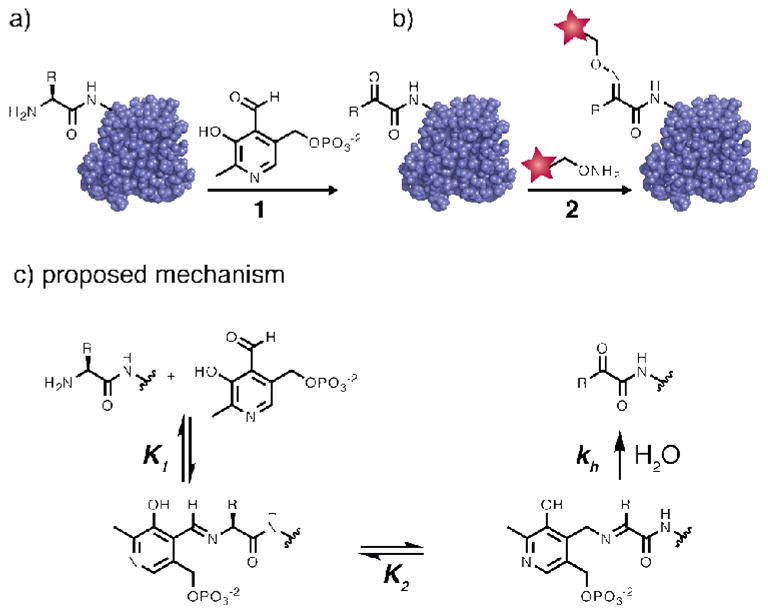
The general scheme of PLP-mediated bioconjugation. (a) In the first step, a protein is incubated with PLP (1) under mild, aqueous conditions. This oxidizes the N-terminus of the protein to a ketone or an aldehyde, providing a unique functional group for further modification. (b) In the second step the ketone is conjugated to an alkoxyamine-bearing reagent (2) through oxime formation. (c) The proposed mechanism begins with Schiff base formation between the N-terminal amine and the PLP aldehyde. Tautomerization, followed by hydrolysis, affords the keto-protein product. Based on this mechanism, the reaction rate is expected to depend on both the concentration of protein and PLP.
