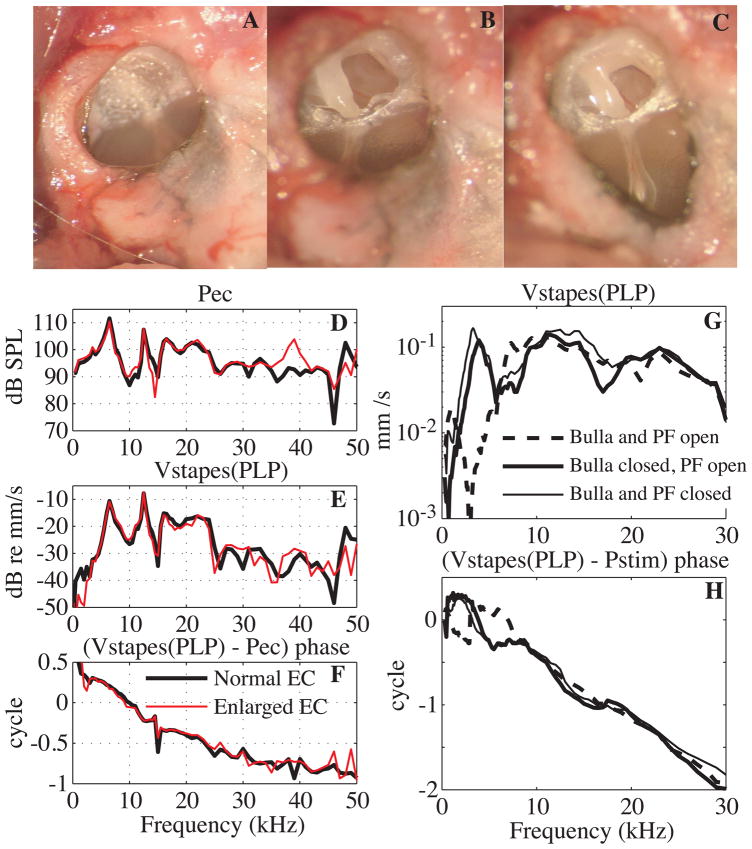
Fig. 3. Surgical approach and its effects (color online).
A: View of the EC entrance with intact PF. B: PF opened widely; the malleus and incus were then visible. C: the EC entrance was enlarged to visualize the manubrium and umbo. D, E, F: Effect of enlarging the EC opening. D: EC pressure close to the umbo. E: stapes velocity, measured at the PLP and denoted stapes(PLP). Conditions as follows: bulla and PF open with a normal (thick black line) and an enlarged (red thin line) EC entrance. F: Stapes(PLP) velocity relative to EC pressure phase (Exp#53, R# 38 and 51). G, H: Effect of the PF opening. G: Stapes(PLP) velocity amplitude. H: Phase relative to the stimulus pressure (Pstim). Conditions as follows: bulla and PF open (dashed line), bulla closed and PF open (thick solid line), bulla and PF closed (thin solid line). (Same experimental data as Fig. 8 in (de La Rochefoucauld et al., 2008): Exp#3 R#18, 26, 28.)