Figure 1.
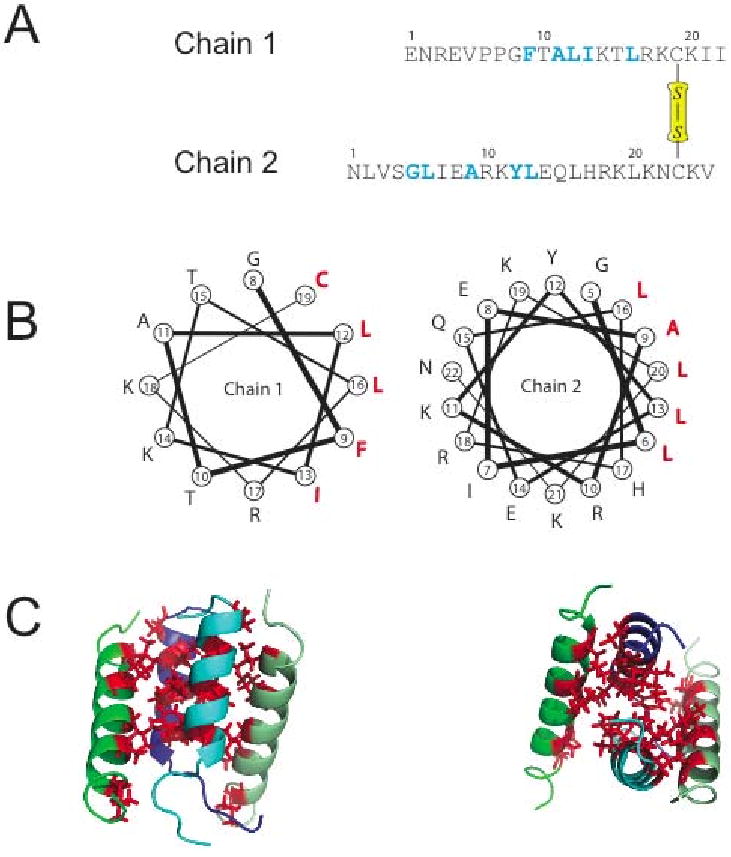
(A) Amino acid sequence of distinctin heterodimer. 15N labeled amino acids are highlighted in blue. Residue Cys-19 of chain 1 and Cys-23 of chain 2 are involved in a disulfide bridge. (B) Helical wheel plots showing the amphipathic nature of each chain. Hydrophobic residues are in red. (C) Three-dimensional structure of distinctin in aqueous buffer [29]. The four-helical bundle is stabilized by hydrophobic interactions of the residues, forming a hydrophobic core in the interior of the structure.
