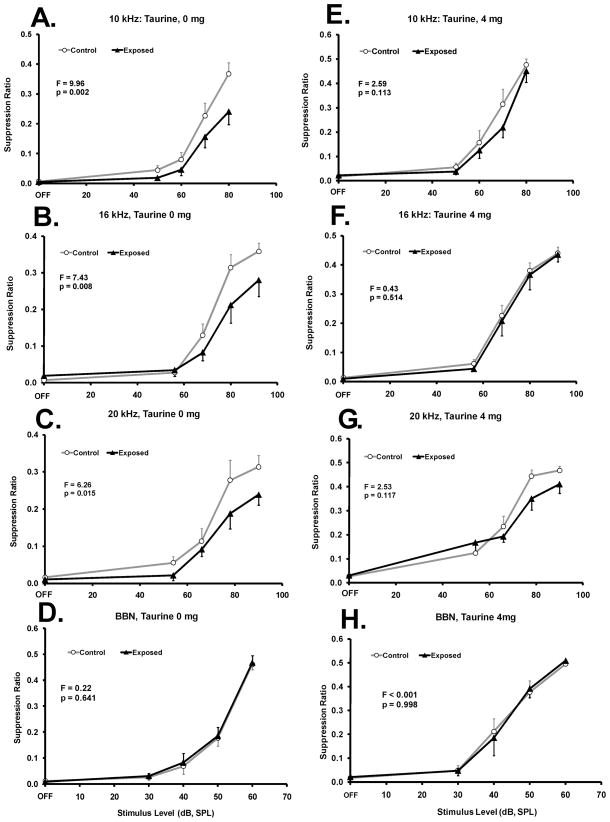
Fig. 2.
Taurine at an average daily dose of 294 mg/kg (4 mg/ml drinking-water concentration is indicated) significantly decreased the evidence of chronic tinnitus in rats. Control n = 8, Exposed n = 6. Performance as a suppression ratio (see text for defininition) is shown as a function of stimulus sound level. Panels A - D show pre-taurine performance (0 mg/ml concentration). Panels E – H show performance on the highest taurine concentration (4 mg/ml). Statistical analysis, between group F tests (df = 1,56), are summarized in each panel; error bars indicate the standard error of the mean.