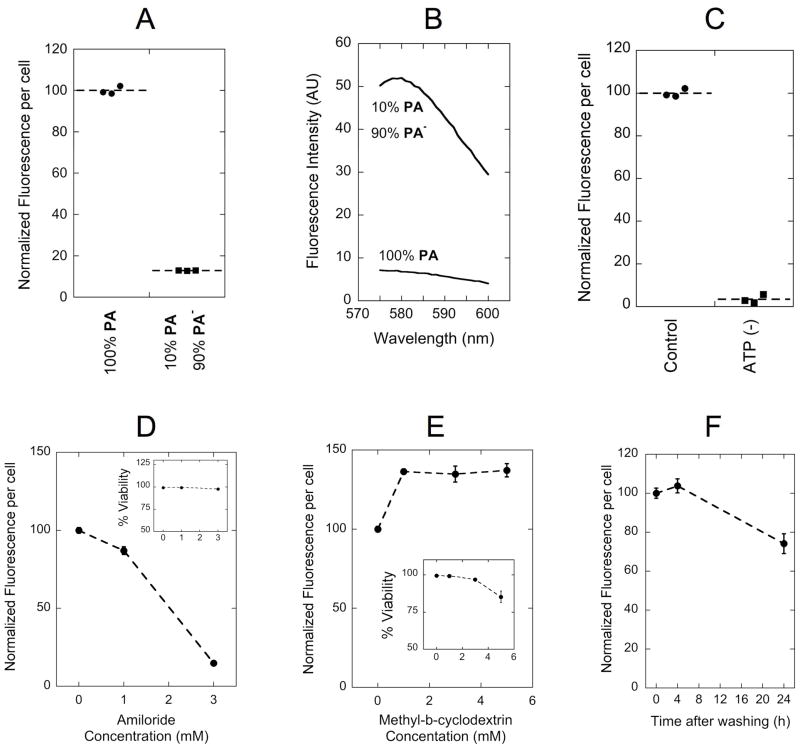
Figure 4. Dissecting double-tail PA internalization mechanism.
(A) Fluorescence intensity per cell was proportional to the amount of labeled monomer (PA) instead of the micelle fluorescence intensity (B): as was shown for a sample prepared with 1/10th of rhodamine content, but 8-fold higher emission intensity. Inhibition of uptake was observed following ATP depletion with a mixture of sodium azide and 2-deoxy-D-glucose (C) and with increasing concentrations of amiloride (D). Methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MβCD) treatment enhanced PA uptake (E). Cell fluorescence per cell was not altered after 4 hours incubation with PA followed by a 4-hour incubation in PA-free medium, indicating lack of considerable exocytosis (F). Insets in (D) and (E) show cell viability in the presence of the corresponding inhibitor. Incubations with PA were performed for 4 h at 37°C in serum supplemented cell culture medium. Data points in (D): (E) and (F) represent the mean +/− standard deviation (n=3).