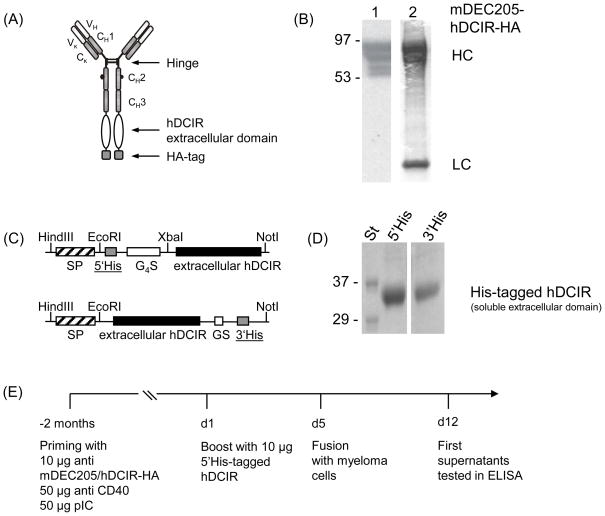
Fig. 1.
Generation of anti hDCIR antibodies. (A) Schematic drawing of the recombinant chimeric anti mouse DEC205/hDCIR-HA antibody. (B) 0.5 μg (left lane, 1), or 2 μg (right lane, 2) of recombinant anti mouse DEC205/hDCIR-HA protein were loaded onto a 4–20% SDS-Page. Protein was detected by Western blot using an anti rat HRP conjugated secondary antibody (1) or directly stained with Coomassie blue (2). The upper bands show the antibody heavy chain (HC), which migrates slower than a normal IgG heavy chain due to the hDCIR fusion. The lower band shows the antibody light chain (LC). The experiment was repeated twice. (C) Scheme of the recombinant 5′ (upper part) and 3′ His-tagged soluble hDCIR expression cassettes (lower part) consisting of mouse IgG1 signaling peptide (SP) ( ), His-tag (6xHis) (
), His-tag (6xHis) ( ), (G4S)2, or GS linker (□), and extracellular hDCIR domain (■). (D) Coomassie gels show purified 5′His-tagged (left) and 3′His-tagged soluble hDCIR protein (right). (E) Timeline of anti hDCIR antibody production. C57BL/6 mice were immunized with 10 μg mDEC205/hDCIR-HA antibody in the presence of 50 μg poly (I:C) and 50 μg anti CD40 stimulating antibody. Mice were boosted with 10 μg soluble 5′His-tagged hDCIR.
), (G4S)2, or GS linker (□), and extracellular hDCIR domain (■). (D) Coomassie gels show purified 5′His-tagged (left) and 3′His-tagged soluble hDCIR protein (right). (E) Timeline of anti hDCIR antibody production. C57BL/6 mice were immunized with 10 μg mDEC205/hDCIR-HA antibody in the presence of 50 μg poly (I:C) and 50 μg anti CD40 stimulating antibody. Mice were boosted with 10 μg soluble 5′His-tagged hDCIR.