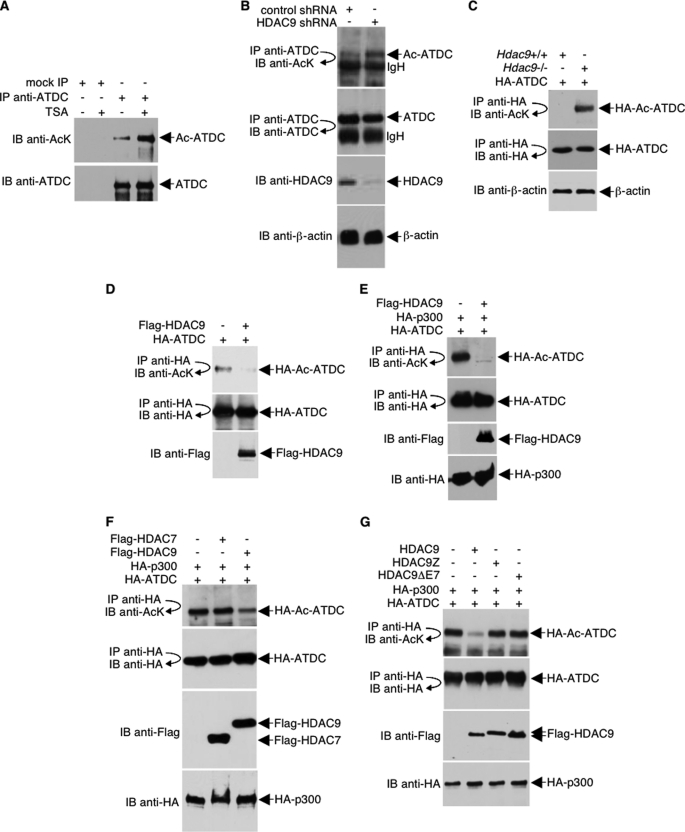
FIGURE 2.
ATDC is deacetylated by HDAC9. A, HeLa cells were treated with TSA (400 ng/ml) or left untreated overnight. Cell lysates were then immunoprecipitated under high stringency conditions with an anti-ATDC antibody. Endogenous acetylated ATDC was analyzed by Western blotting with an anti-acetyl-lysine antibody. A Western blot was also performed with anti-ATDC to assess the ATDC immunoprecipitation efficiency. B, 293T cells were transfected with either HDAC9 shRNA or control shRNA. Following immunoprecipitation with anti-ATDC antibodies, Western blots were performed with the indicated antibodies to assess the acetylation of endogenous ATDC and ATDC immunoprecipitation efficiency. Western blots were also performed with the indicated antibodies to assess the levels of HDAC9 and β-actin expression. C, murine Hdac9+/+ and Hdac9−/− fibroblasts were transfected with HA-ATDC expression plasmids, and cell lysates were collected and analyzed by immunoprecipitation with an anti-HA antibody and Western blotting with an anti-acetyl-lysine antibody. The blot was stripped and reprobed with anti-HA to confirm equal HA-ATDC protein levels. A Western blot was also performed with an anti-β-actin antibody to confirm equal loading. D–G, HeLa cells were co-transfected with plasmids that express HA-ATDC and HA-p300 (or HA vector) in the presence or absence of co-transfection with FLAG-HDAC7 or different FLAG-HDAC9 plasmids. The acetylation of HA-ATDC and the expression levels of different proteins were determined with direct Western blot or immunoprecipitations and then followed by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. IP, immunoprecipitation; IB, immunoblot.