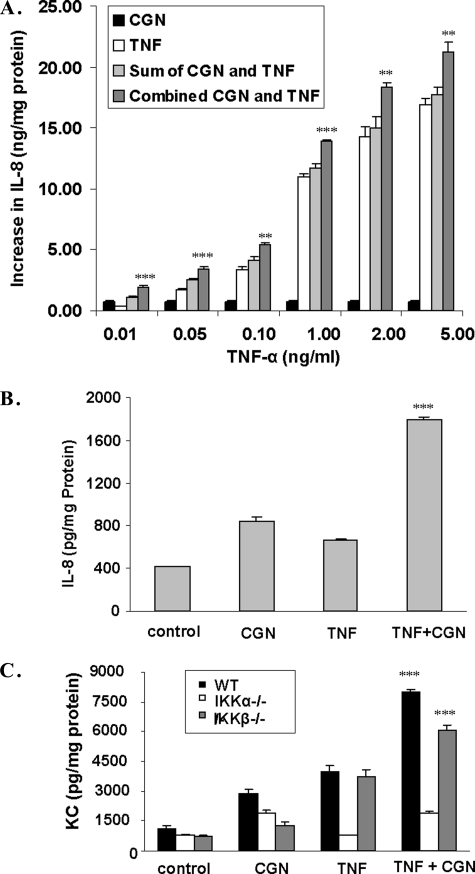
FIGURE 1.
TNF-α and CGN produced synergistic increases in IL-8 or KC secretion. A, IL-8 secretion was measured by ELISA in the spent media of NCM460 cells following stimulation by either TNF-α (at concentrations ranging from 0.01 to 5 ng/ml) or CGN (1 μg/ml) or their combination for 24 h. The increase from the base-line value (base line = 0.623 ± 0.06 ng/mg protein) is represented on the y axis. At all of the concentrations of TNF-α tested, exposure to the combination of TNF-α and CGN stimulated the IL-8 secretion to a significantly greater value than the sum of the increases of the individual exposures (all p values <0.01, unpaired t test, two-tailed). B, similarly, the increase in IL-8 secretion in primary human colonic epithelial cells was significantly greater following the combined exposure to CGN (1 μg/ml) and TNF-α (0.01 ng/ml) for 24 h (1.386 ± 0.024 ng/mg protein; p < 0.0001, unpaired t test, two-tailed) than the sum (0.686 ± 0.034 ng/mg protein) of the increases from exposure to CGN and TNF-α individually. C, in the MEF, KC, the mouse homolog of IL-8, increased synergistically in response to TNF-α and CGN in the WT and IKKβ−/− cells (p = 0.0004 and p = 0.0006, respectively; unpaired t test, two-tailed) but not in the IKKα−/− cells. **, p ≤ 0.01; ***, p ≤ 0.001. Error bars, S.D.