FIGURE 2.
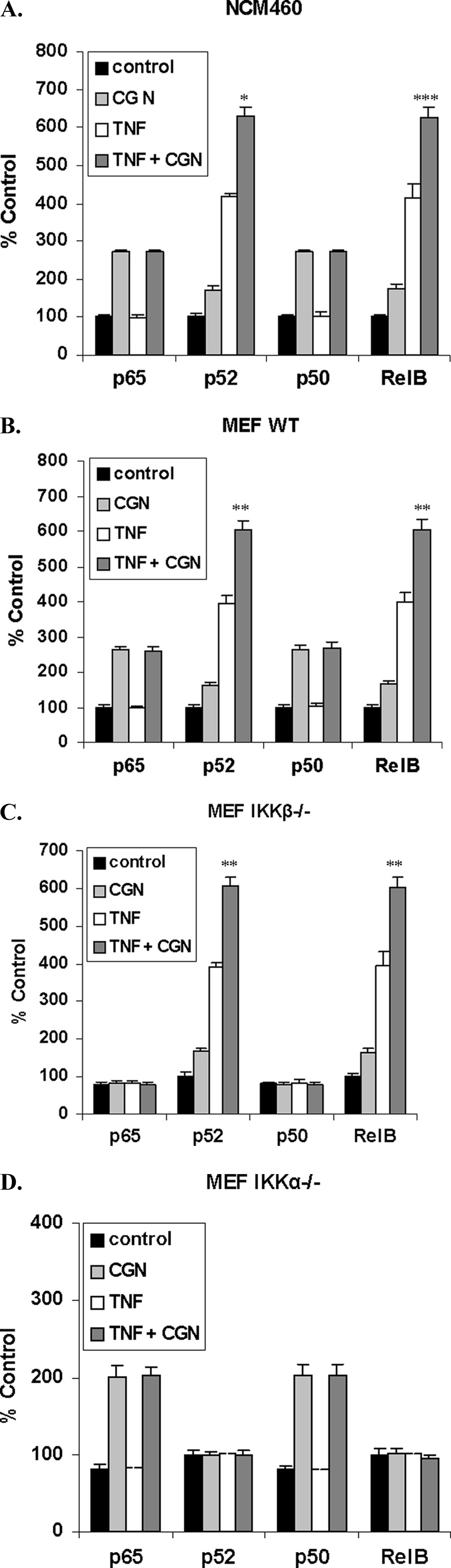
TNF-α and CGN in combination increased p52 and RelB beyond an additive effect, but p65 (RelA) and p50 did not increase. A, nuclear content of NF-κB components was measured by oligonucleotide ELISA. In the NCM460 nuclear extracts, combined λCGN (1 μg/ml) and TNF-α (0.1 ng/ml) exposure for 24 h significantly increased the nuclear p52 and RelB (p = 0.019 and p = 0.0005, respectively; unpaired t test, two-tailed). TNF-α exposure produced no increases in either p65 or p50 over the control, and no synergistic increases occurred in p65 or p50 with the combination of CGN and TNF-α. B, similarly, in the WT MEF, CGN and TNF-α in combination increased the nuclear p52 and RelB significantly beyond the sum of the increases induced by CGN and TNF-α individually (p = 0.0016 and 0.0041, unpaired t test, two-tailed). C, in the IKKβ−/− MEF, CGN and TNF-α in combination significantly increased the nuclear p52 and RelB, beyond the sum of the CGN-induced and TNF-α-induced increases (p = 0.008 and p = 0.0013, unpaired t test, two-tailed), as in the NCM460 and the WT MEF. D, in contrast, in the IKKα−/− cells, the combination of CGN and TNF-α produced no further increases in NF-κB components. *, p ≤ 0.05; **, p ≤ 0.01; ***, p ≤ 0.001. Error bars, S.D.
